目錄¶
@[toc]
前言¶
這次使用一個貓的數據集,我們使用深度神經網絡來識別這個是貓或者不是貓。

導包¶
這裏導入了兩個工具類,可以從這裏下載,這裏包含了這個函數和用到的數據集,其中用到了h5py,如果讀者沒有安裝的話,要先用pip安裝這個庫,還有以下用到的庫也要安裝。
# coding=utf-8
from dnn_utils_v2 import sigmoid, sigmoid_backward, relu, relu_backward
from lr_utils import load_dataset
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import scipy
from scipy import ndimage
初始化網絡參數¶
在網絡定義之前,需要先對網絡的參數進行初始化,這裏分兩個來初始化,一個是兩層網絡的,另一個是L層網絡的。
兩層網絡的初始化¶
對兩層網絡的參數初始化要用到輸入層的大小、隱藏層的大小、輸出層的大小。
def initialize_parameters(n_x, n_h, n_y):
"""
初始化參數
:param n_x: 輸入層的大小。
:param n_h: 隱藏層的大小。
:param n_y: 輸出層的大小。
:return:
parameters -- 包含您的參數的python字典:
W1 -- 形狀重量矩陣(n_h, n_x)
b1 -- 形狀的偏置向量(n_h, 1)
W2 -- 形狀重量矩陣(n_y, n_h)
b2 -- 形狀的偏置向量(n_y, 1)
"""
W1 = np.random.randn(n_h, n_x) * 0.01
b1 = np.zeros((n_h, 1))
W2 = np.random.randn(n_y, n_h) * 0.01
b2 = np.zeros((n_y, 1))
assert (W1.shape == (n_h, n_x))
assert (b1.shape == (n_h, 1))
assert (W2.shape == (n_y, n_h))
assert (b2.shape == (n_y, 1))
parameters = {"W1": W1,
"b1": b1,
"W2": W2,
"b2": b2}
return parameters
L層網絡的初始化¶
對於更深的網絡,需要的參數是網絡中每一層的尺寸的python數組。相關的計算如下:
| | Shape of W | Shape of b | Activation | Shape of Activation
:—: | :—: | :—: | :—: | :—:
| Layer 1 | \((n^{[1]},12288)\) | \((n^{[1]},1)\) | $Z^{[1]} = W^{[1]} X + b^{[1]} $ | \((n^{[1]},209)\)
|Layer 2|\((n^{[2]}, n^{[1]})\)|\((n^{[2]},1)\)|\(Z^{[2]} = W^{[2]} A^{[1]} + b^{[2]}\)|\((n^{[2]}, 209)\)
|\(\vdots\)|\(\vdots\)|\(\vdots\)|\(\vdots\)|\(\vdots\)
|Layer L-1|\((n^{[L-1]}, n^{[L-2]})\)|\((n^{[L-1]}, 1)\)|\(Z^{[L-1]} = W^{[L-1]} A^{[L-2]} + b^{[L-1]}\)|\((n^{[L-1]}, 209)\)
|Layer L|\((n^{[L]}, n^{[L-1]})\)| \((n^{[L]}, 1)\)|\(Z^{[L]} = W^{[L]} A^{[L-1]} + b^{[L]}\)|\((n^{[L]}, 209)\)
def initialize_parameters_deep(layer_dims):
"""
初始化深度參數
:param layer_dims: 包含我們網絡中每一層的尺寸的python數組(列表)。
:return:
parameters -- python字典包含參數的"W1", "b1", ..., "WL", "bL":
Wl -- 形狀權重矩陣(layer_dims[l], layer_dims[l-1])
bl -- 形狀偏差向量(layer_dims[l], 1)
"""
parameters = {}
L = len(layer_dims) # number of layers in the network
for l in range(1, L):
parameters['W' + str(l)] = np.random.randn(layer_dims[l], layer_dims[l - 1]) / np.sqrt(
layer_dims[l - 1]) # *0.01
parameters['b' + str(l)] = np.zeros((layer_dims[l], 1))
assert (parameters['W' + str(l)].shape == (layer_dims[l], layer_dims[l - 1]))
assert (parameters['b' + str(l)].shape == (layer_dims[l], 1))
return parameters
正向傳播模塊¶
一個完整的神經網絡流程是如圖所示:
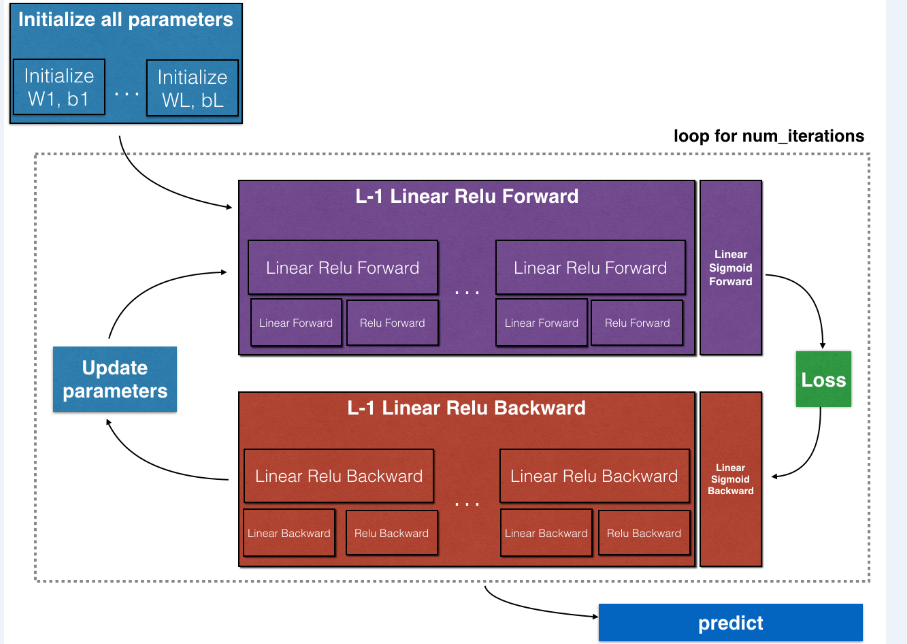
在這一部分,我們要完成的是紫色部分的正向傳播,其中包括線性正向傳播、線性激活正向傳播和完成整個正向傳播的L層模型正向傳播。
線性正向傳播¶
構建前向傳播的線性部分,使用的線性公式如下:
\(\(Z^{[l]} = W^{[l]}A^{[l-1]} +b^{[l]}\tag{1}\)\)
def linear_forward(A, W, b):
"""
實現一個層的正向傳播的線性部分。
:param A: 前一層(或輸入數據)的激活:(前一層的大小,示例的數量)
:param W: 權重矩陣:形狀的numpy數組(當前層的大小,上一層的大小)
:param b: 偏置向量,形狀的numpy數組(當前層的大小,1)
:return:
Z -- 激活函數的輸入,也稱爲預激活參數。
cache -- :包含“a”、“W”和“b”的python字典;存儲用於有效地計算向後傳遞。
"""
Z = np.dot(W, A) + b
assert (Z.shape == (W.shape[0], A.shape[1]))
cache = (A, W, b)
return Z, cache
線性激活正向傳播¶
這裏使用到了兩個激活函數:
- Sigmoid:\(\sigma(Z) = \sigma(W A + b) = \frac{1}{ 1 + e^{-(W A + b)}}\)
- ReLU:\(A = ReLU(Z) = max(0, Z)\)
從線性到激活使用到的公式如下:
\(\(A^{[l]} = g(Z^{[l]}) = g(W^{[l]}A^{[l-1]} +b^{[l]})\tag{2}\)\)
def linear_activation_forward(A_prev, W, b, activation):
"""
實現線性->激活層的正向傳播。
:param A_prev: 前一層(或輸入數據)的激活:(前一層的大小,示例的數量)
:param W: 權重矩陣:形狀的numpy數組(當前層的大小,上一層的大小)
:param b: 偏置向量,形狀的numpy數組(當前層的大小,1)
:param activation: 在此層中使用的激活,存儲爲文本字符串:“sigmoid”或“relu”
:return:
A -- 激活函數的輸出,也稱爲激活後值。
cache --包含“線性緩存”和“activation_cache”的python字典;
存儲用於有效地計算向後傳遞
"""
if activation == "sigmoid":
Z, linear_cache = linear_forward(A_prev, W, b)
A, activation_cache = sigmoid(Z)
elif activation == "relu":
Z, linear_cache = linear_forward(A_prev, W, b)
A, activation_cache = relu(Z)
assert (A.shape == (W.shape[0], A_prev.shape[1]))
cache = (linear_cache, activation_cache)
return A, cache
L層模型正向傳播¶
根據線性正向傳播和線性激活正向傳播的循環L次,得到一個L層的模型,如下圖:
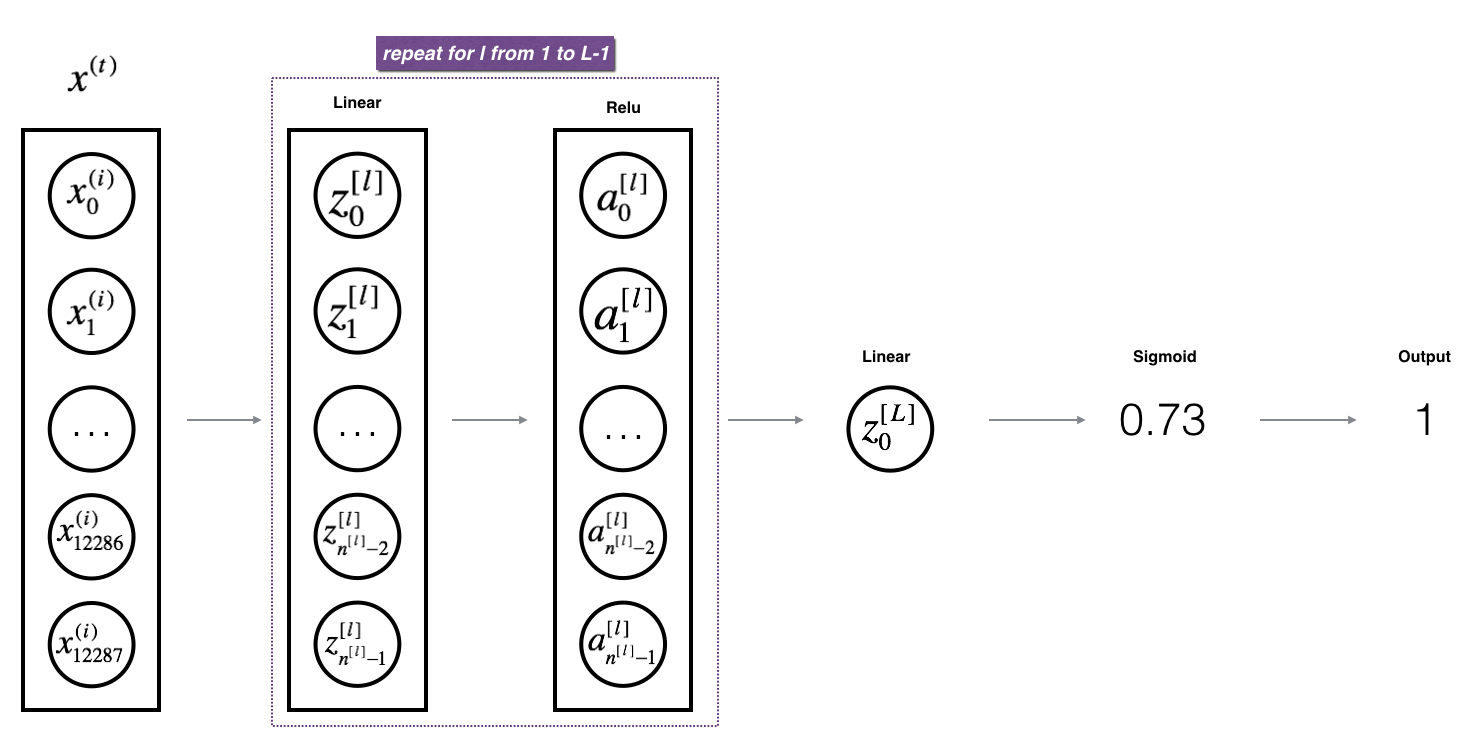
代碼中使用到的AL是指公式的\(A^{[L]}\):
\(\(A^{[L]} = \sigma(Z^{[L]}) = \sigma(W^{[L]} A^{[L-1]} + b^{[L]})\tag{3}\)\)
def L_model_forward(X, parameters):
"""
爲[LINEAR->RELU]*(L-1)->LINEAR->SIGMOID計算實現正向傳播。
:param X: 數據,形狀的numpy數組(輸入大小,示例數量)
:param parameters: initialize_parameters_deep()的輸出
:return:
AL -- 最後激活後值
caches -- 緩存包含列表:
線性_activation_forward()的每個緩存(其中有L-1,從0到L-1的索引)
"""
caches = []
A = X
L = len(parameters) // 2 # number of layers in the neural network
# Implement [LINEAR -> RELU]*(L-1). Add "cache" to the "caches" list.
for l in range(1, L):
A_prev = A
A, cache = linear_activation_forward(A_prev, parameters['W' + str(l)], parameters['b' + str(l)],
activation="relu")
caches.append(cache)
# Implement LINEAR -> SIGMOID. Add "cache" to the "caches" list.
AL, cache = linear_activation_forward(A, parameters['W' + str(L)], parameters['b' + str(L)], activation="sigmoid")
caches.append(cache)
assert (AL.shape == (1, X.shape[1]))
return AL, caches
計算損失函數¶
計算成本函數的公式如下:
\(\(cost = -\frac{1}{m} \sum\limits_{i = 1}^{m} (y^{(i)}\log\left(a^{[L] (i)}\right) + (1-y^{(i)})\log\left(1- a^{[L](i)}\right)) \tag{4}\)\)
def compute_cost(AL, Y):
"""
實現由公式(7)定義的成本函數。
:param AL: 對應於你的標籤預測的概率向量,形狀(1,例子數)
:param Y: 正確的“標籤”矢量(例如:如果非cat,則包含0)、形狀(1、示例數量)
:return:
cost -- 交叉熵損失
"""
m = Y.shape[1]
cost = -(np.sum(np.dot(Y, np.log(AL).T) + np.dot((1 - Y), np.log(1 - AL).T))) / m
cost = np.squeeze(cost)
assert (cost.shape == ())
return cost
反向傳播模塊¶
就像向前傳播一樣,實現反向傳播的輔助函數。反向傳播用於計算損失函數與參數的梯度
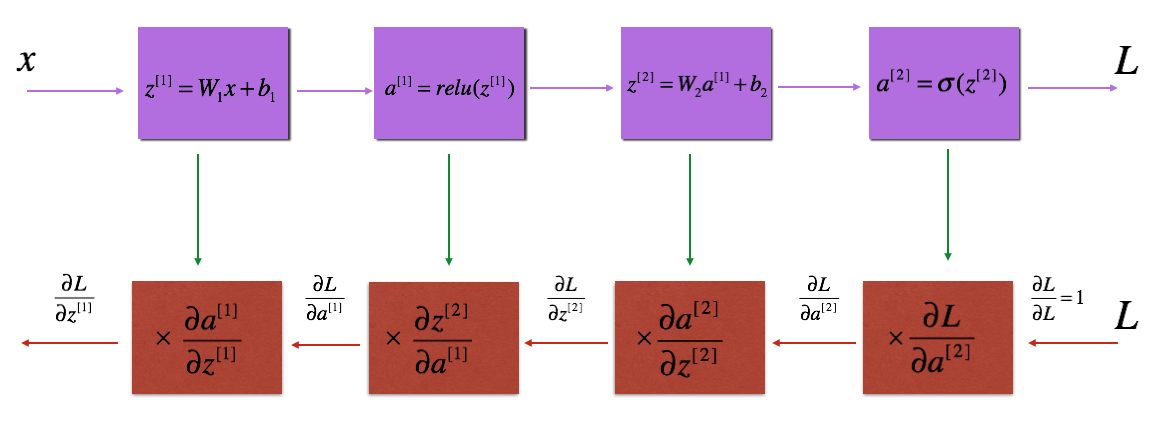
線性反向傳播¶
在反向傳播的時候使用到公式如下:
$$ dW^{[l]} = \frac{\partial \mathcal{L} }{\partial W^{[l]}} = \frac{1}{m} dZ^{[l]} A^{[l-1] T} \tag{5}$$
$$ db^{[l]} = \frac{\partial \mathcal{L} }{\partial b^{[l]}} = \frac{1}{m} \sum_{i = 1}^{m} dZ^{l}\tag{6}$$
$$ dA^{[l-1]} = \frac{\partial \mathcal{L} }{\partial A^{[l-1]}} = W^{[l] T} dZ^{[l]} \tag{7}$$
def linear_backward(dZ, cache):
"""
實現單層(l層)反向傳播的線性部分
:param dZ: 線性輸出(當前層l)的成本梯度
:param cache: 來自當前層的正向傳播元組(A_prev, W, b)的值
:return:
dA_prev -- 關於激活(前一層l-1)的成本梯度,與A_prev相同。
dW -- 關於W(當前層l)的成本梯度,與W相同。
db -- :b(當前層l)的成本梯度,與b相同。
"""
A_prev, W, b = cache
m = A_prev.shape[1]
dW = np.dot(dZ, A_prev.T) / m
db = np.sum(dZ, axis=1, keepdims=True) / m
dA_prev = np.dot(W.T, dZ)
assert (dA_prev.shape == A_prev.shape)
assert (dW.shape == W.shape)
assert (db.shape == b.shape)
return dA_prev, dW, db
線性激活反向傳播¶
在這裏使用到的計算公式如下:
\(\(dZ^{[l]} = dA^{[l]} * g'(Z^{[l]}) \tag{8}\)\)
def linear_activation_backward(dA, cache, activation):
"""
實現 線性->激活層 的反向傳播。
:param dA: 當前層的激活梯度
:param cache: 我們存儲的值的元組(線性緩存,activation_cache)可以有效地計算反向傳播。
:param activation: 在此層中使用的激活,存儲爲文本字符串:“sigmoid”或“relu”
:return:
dA_prev -- 關於激活(前一層l-1)的成本梯度,與A_prev相同。
dW -- 關於W(當前層l)的成本梯度,與W相同。
db -- b(當前層l)的成本梯度,與b相同。
"""
linear_cache, activation_cache = cache
if activation == "relu":
dZ = relu_backward(dA, activation_cache)
dA_prev, dW, db = linear_backward(dZ, linear_cache)
elif activation == "sigmoid":
dZ = sigmoid_backward(dA, activation_cache)
dA_prev, dW, db = linear_backward(dZ, linear_cache)
return dA_prev, dW, db
L層模型反向傳播¶
L層模型反向傳播的流程,如圖所示:
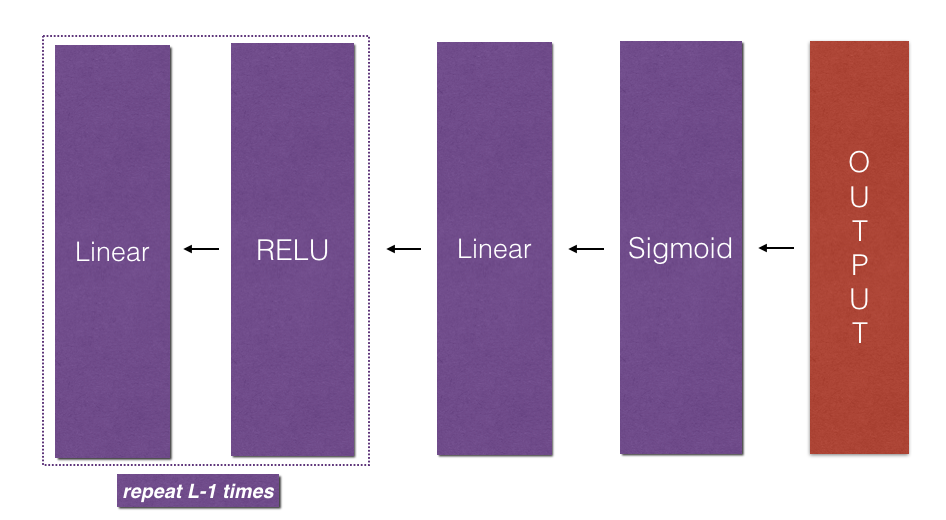
使用這個公式實現反向傳播:
$$grads[“dW” + str(l)] = dW^{[l]}\tag{9} $$
def L_model_backward(AL, Y, caches):
"""
實現[線性->RELU] * (L-1) ->線性-> SIGMOID組的反向傳播。
:param AL: 概率向量,正向傳播的輸出(L_model_forward())
:param Y: true“label”vector(如果非cat,則包含0)
:param caches: 緩存包含列表:
所有的緩存來自linear_activation_forward()的"relu" (它是caches[l], for l in range(L-1) i.e l = 0...L-2)
緩存來自linear_activation_forward()的"sigmoid" (它是caches[L-1])
:return: 梯度字典:
grads["dA" + str(l)]
grads["dW" + str(l)]
grads["db" + str(l)]
"""
grads = {}
L = len(caches) # the number of layers
m = AL.shape[1]
Y = Y.reshape(AL.shape) # after this line, Y is the same shape as AL
# Initializing the backpropagation
dAL = - (np.divide(Y, AL) - np.divide(1 - Y, 1 - AL))
# Lth layer (SIGMOID -> LINEAR) gradients. Inputs: "AL, Y, caches". Outputs: "grads["dAL"], grads["dWL"], grads["dbL"]
current_cache = caches[L - 1]
grads["dA" + str(L - 1)], grads["dW" + str(L)], grads["db" + str(L)] = linear_activation_backward(dAL,
current_cache,
activation="sigmoid")
for l in reversed(range(L - 1)):
# lth layer: (RELU -> LINEAR) gradients.
current_cache = caches[l]
dA_prev_temp, dW_temp, db_temp = linear_activation_backward(grads["dA" + str(l + 1)], current_cache,
activation="relu")
grads["dA" + str(l)] = dA_prev_temp
grads["dW" + str(l + 1)] = dW_temp
grads["db" + str(l + 1)] = db_temp
return grads
更新模型參數¶
使用梯度下降來更新模型的參數,使用到的公式如下:
$$ W^{[l]} = W^{[l]} - \alpha \text{ } dW^{[l]} \tag{10}$$
$$ b^{[l]} = b^{[l]} - \alpha \text{ } db^{[l]} \tag{11}$$
def update_parameters(parameters, grads, learning_rate):
"""
使用梯度下降來更新參數。
:param parameters: 包含參數的python字典。
:param grads: 包含您的梯度的python字典,l_model_back的輸出。
:param learning_rate: 學習率
:return:
parameters -- 包含更新參數的python字典。
parameters["W" + str(l)]
parameters["b" + str(l)]
"""
L = len(parameters) // 2 # number of layers in the neural network
for l in range(L):
parameters["W" + str(l + 1)] = parameters["W" + str(l + 1)] - learning_rate * grads["dW" + str(l + 1)]
parameters["b" + str(l + 1)] = parameters["b" + str(l + 1)] - learning_rate * grads["db" + str(l + 1)]
return parameters
預測正確率¶
通過傳入數據和對於的標籤,還有模型參數就可以預測數據並計算準確率了。
def predict(X, y, parameters):
"""
該函數用於預測l層神經網絡的結果。
:param X: 您想要標記的示例數據集。
:param y: 正確的標籤
:param parameters: 訓練模式的參數。
:return:
p -- 對給定數據集X的預測。
"""
m = X.shape[1]
n = len(parameters) // 2 # 神經網絡中的層數。
p = np.zeros((1, m))
# 正向傳播
probas, caches = L_model_forward(X, parameters)
# 將檢驗結果轉換爲0/1預測。
for i in range(0, probas.shape[1]):
if probas[0, i] > 0.5:
p[0, i] = 1
else:
p[0, i] = 0
m = float(m)
print("Accuracy: " + str(np.sum((p == y) / m)))
return p
兩層神經網絡模型¶
構建一個具有以下結構的2層神經網絡:LINEAR - > RELU - > LINEAR - > SIGMOID。
def two_layer_model(X, Y, layers_dims, learning_rate=0.0075, num_iterations=3000, print_cost=False):
"""
實現了兩層神經網絡:LINEAR>RELU->LINEAR->SIGMOID。
:param X: 輸入數據,形狀(n_x,示例數量)
:param Y: 真正的“標籤”向量(包含0如果貓,1如果是非貓),形狀(1,例子數量)
:param layers_dims: 層的維數(n_x, n_h, n_y)
:param learning_rate: 梯度下降更新規則的學習速率
:param num_iterations: 優化循環的迭代次數。
:param print_cost: 如果設置爲True,則每100次迭代將打印成本。
:return:
parameters -- 包含W1、W2、b1和b2的字典
"""
grads = {}
costs = []
m = X.shape[1] # number of examples
(n_x, n_h, n_y) = layers_dims
parameters = initialize_parameters(n_x, n_h, n_y)
W1 = parameters["W1"]
b1 = parameters["b1"]
W2 = parameters["W2"]
b2 = parameters["b2"]
# 循環(梯度下降)
for i in range(0, num_iterations):
# 正向傳播: LINEAR -> RELU -> LINEAR -> SIGMOID
A1, cache1 = linear_activation_forward(X, W1, b1, activation="relu")
A2, cache2 = linear_activation_forward(A1, W2, b2, activation="sigmoid")
# 計算損失
cost = compute_cost(A2, Y)
# 初始化反向傳播
dA2 = - (np.divide(Y, A2) - np.divide(1 - Y, 1 - A2))
# 反向傳播
dA1, dW2, db2 = linear_activation_backward(dA2, cache2, activation="sigmoid")
dA0, dW1, db1 = linear_activation_backward(dA1, cache1, activation="relu")
grads['dW1'] = dW1
grads['db1'] = db1
grads['dW2'] = dW2
grads['db2'] = db2
# 更新參數。
parameters = update_parameters(parameters, grads, learning_rate)
W1 = parameters["W1"]
b1 = parameters["b1"]
W2 = parameters["W2"]
b2 = parameters["b2"]
# 打印每100個培訓實例的成本。
if print_cost and i % 100 == 0:
print("Cost after iteration {}: {}".format(i, np.squeeze(cost)))
if print_cost and i % 100 == 0:
costs.append(cost)
# plot the cost
plt.plot(np.squeeze(costs))
plt.ylabel('cost')
plt.xlabel('iterations (per tens)')
plt.title("Learning rate =" + str(learning_rate))
plt.show()
return parameters
L層神經網絡模型¶
構建一個 該該 具有以下結構的L層狀神經網絡:[LINEAR→RELU] * (L-1) - > LINEAR - > SIGMOID
def L_layer_model(X, Y, layers_dims, learning_rate=0.0075, num_iterations=3000, print_cost=False):
"""
實現一個l層神經網絡:[LINEAR->RELU]*(L-1)->LINEAR->SIGMOID。
:param X: 數據,形狀的numpy數組(示例的數量,num_px * num_px * 3)
:param Y: :真正的“標籤”向量(包含0如果貓,1如果是非貓),形狀(1,例子數量)
:param layers_dims: 包含輸入大小和每層長度的列表(層數+ 1)。
:param learning_rate: 梯度下降更新規則的學習速率。
:param num_iterations: 優化循環的迭代次數。
:param print_cost: 如果是真的,它將每100步打印成本。
:return:
parameters -- 由模型學習的參數。他們可以被用來預測。
"""
costs = []
parameters = initialize_parameters_deep(layers_dims)
# 循環(梯度下降)
for i in range(0, num_iterations):
# 正向傳播: [LINEAR -> RELU]*(L-1) -> LINEAR -> SIGMOID.
AL, caches = L_model_forward(X, parameters)
# 計算損失
cost = compute_cost(AL, Y)
# 反向傳播.
grads = L_model_backward(AL, Y, caches)
# 更新參數。
parameters = update_parameters(parameters, grads, learning_rate)
# 打印每100個培訓實例的成本。
if print_cost and i % 100 == 0:
print ("Cost after iteration %i: %f" % (i, cost))
if print_cost and i % 100 == 0:
costs.append(cost)
# plot the cost
plt.plot(np.squeeze(costs))
plt.ylabel('cost')
plt.xlabel('iterations (per tens)')
plt.title("Learning rate =" + str(learning_rate))
plt.show()
return parameters
預測自己的圖像¶
這個函數是用來預測自己的圖像的,可以自行修剪圖像的大小,滿足訓練時的大小。
def infer_image(my_image,parameters,num_px):
my_label_y = [1] # the true class of your image (1 -> cat, 0 -> non-cat)
fname = "images/" + my_image
image = np.array(ndimage.imread(fname, flatten=False))
my_image = scipy.misc.imresize(image, size=(num_px, num_px)).reshape((num_px * num_px * 3, 1))
my_image = my_image / 255.
my_predicted_image = predict(my_image, my_label_y, parameters)
plt.imshow(image)
print ("y = " + str(np.squeeze(my_predicted_image)) + ", your L-layer model predicts a \"" + classes[
int(np.squeeze(my_predicted_image)),].decode("utf-8") + "\" picture.")
模型的使用¶
這使用兩種模型,一個是兩層的模型,另一個是L層的模型。
兩層模型的使用¶
使用兩層神經網絡優化參數
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 獲取數據
train_x_orig, train_y, test_x_orig, test_y, classes = load_dataset()
# 重塑培訓和測試範例。
train_x_flatten = train_x_orig.reshape(train_x_orig.shape[0], -1).T
test_x_flatten = test_x_orig.reshape(test_x_orig.shape[0], -1).T
# 將數據標準化,使其具有0到1之間的特徵值
train_x = train_x_flatten / 255.
test_x = test_x_flatten / 255.
layers_dims_two = (12288, 7, 1) # n_x = num_px * num_px * 3
parameters = two_layer_model(train_x, train_y, layers_dims_two, num_iterations=2500, print_cost=True)
predictions_train = predict(train_x, train_y, parameters)
predictions_test = predict(test_x, test_y, parameters)
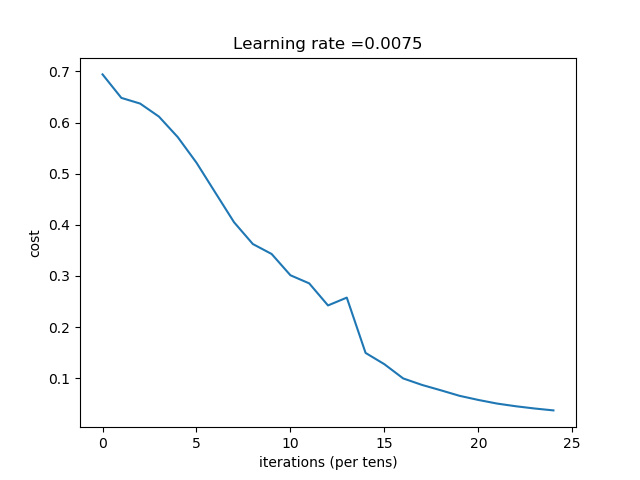
運行後輸出的結果是:
Cost after iteration 0: 0.694163741553
Cost after iteration 100: 0.648266362508
Cost after iteration 200: 0.637126344142
Cost after iteration 300: 0.611710351257
.......
Cost after iteration 2100: 0.0505762788807
Cost after iteration 2200: 0.0453126197353
Cost after iteration 2300: 0.0409255847312
Cost after iteration 2400: 0.0372231796013
Accuracy: 1.0
Accuracy: 0.68
其對應的折線圖:
L層模型的使用¶
使用深度神經網絡優化參數:
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 獲取數據
train_x_orig, train_y, test_x_orig, test_y, classes = load_dataset()
# 重塑培訓和測試範例。
train_x_flatten = train_x_orig.reshape(train_x_orig.shape[0], -1).T
test_x_flatten = test_x_orig.reshape(test_x_orig.shape[0], -1).T
# 將數據標準化,使其具有0到1之間的特徵值
train_x = train_x_flatten / 255.
test_x = test_x_flatten / 255.
layers_dims_l = [12288, 20, 7, 5, 1]
parameters = L_layer_model(train_x, train_y, layers_dims_l, num_iterations=2500, print_cost=True)
pred_train = predict(train_x, train_y, parameters)
pred_test = predict(test_x, test_y, parameters)
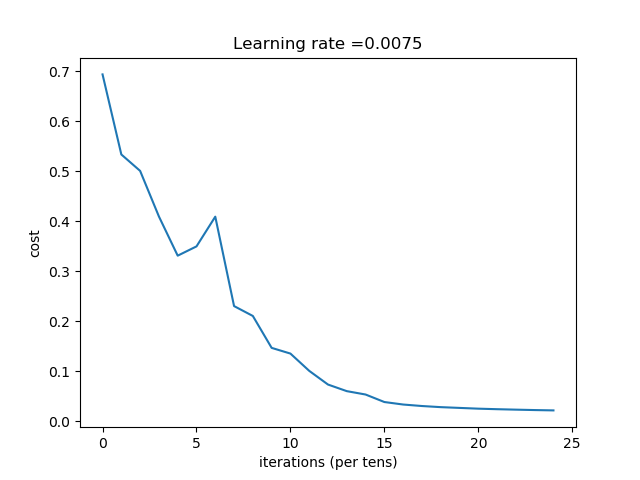
深度神經網絡輸出的日誌如下:
Cost after iteration 0: 0.693828
Cost after iteration 100: 0.533567
Cost after iteration 200: 0.500737
Cost after iteration 300: 0.409495
.....
Cost after iteration 2100: 0.023786
Cost after iteration 2200: 0.022884
Cost after iteration 2300: 0.022056
Cost after iteration 2400: 0.021382
Accuracy: 0.980861244019
Accuracy: 0.7
其對應的折線圖如下:
預測自己的圖像¶
訓練好的模型也可以用來預測模型自己的圖像:
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 獲取數據
train_x_orig, train_y, test_x_orig, test_y, classes = load_dataset()
# 重塑培訓和測試範例。
train_x_flatten = train_x_orig.reshape(train_x_orig.shape[0], -1).T
test_x_flatten = test_x_orig.reshape(test_x_orig.shape[0], -1).T
# 將數據標準化,使其具有0到1之間的特徵值
train_x = train_x_flatten / 255.
test_x = test_x_flatten / 255.
layers_dims_l = [12288, 20, 7, 5, 1]
parameters = L_layer_model(train_x, train_y, layers_dims_l, num_iterations=2500, print_cost=True)
infer_image('images/cat2.jpg', parameters, train_x_orig.shape[1])
預測的結果如下:
y = 1.0, your L-layer model predicts a "cat" picture.
參考資料¶
- http://deeplearning.ai/
該筆記是學習吳恩達老師的課程寫的。初學者入門,如有理解有誤的,歡迎批評指正!