均值(mean,average)¶
- 代表一組數據在分佈上的集中趨勢和總體上的平均水平。
- 常說的中心化(Zero-Centered)或者零均值化(Mean-subtraction),就是把每個數值都減去均值。
\[\mu=\frac{1}{N}\sum_{i=1}^Nx_i\left(x:x_1,x_2,...,x_N\right)\]
import numpy as np
# 一維數組
x = np.array([-0.02964322, -0.11363636, 0.39417967, -0.06916996, 0.14260276])
print('數據:', x)
# 求均值
avg = np.mean(x)
print('均值:', avg)
輸出:
數據: [-0.02964322 -0.11363636 0.39417967 -0.06916996 0.14260276]
均值: 0.064866578
標準差(Standard Deviation)¶
- 代表一組數據在分佈上第離散程度。
- 方差是標準差的平方。
\(\(\sigma=\sqrt{\frac{1}{N}\sum_{i=1}^N\left(x_i-\mu\right)^2} \left(x:x_1,x_2,...,x_N\right)\)\)
import numpy as np
# 一維數組
x = np.array([-0.02964322, -0.11363636, 0.39417967, -0.06916996, 0.14260276])
print('數據:', x)
# 求標準差
std = np.std(x)
print('標準差:', std)
輸出:
數據: [-0.02964322 -0.11363636 0.39417967 -0.06916996 0.14260276]
標準差: 0.18614576055671836
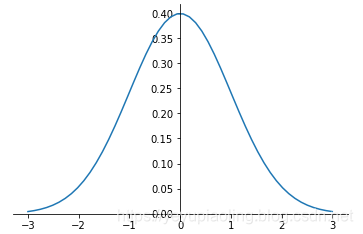
正態分佈(Normal Distribution)¶
- 又叫“常態分佈”,“高斯分佈”,是最重要的一種分佈。
- 均值決定位置,方差決定幅度。
- 表示:\(X\sim N\left(\mu,\sigma^2\right)\)
正態分佈的概率密度函數:
\(\(f(x)=\frac{1}{\sqrt {2\pi\sigma}}e^{-\frac{\left(x-\mu\right)^2}{2\sigma^2}}\)\)
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
def nd(x, u=-0, d=1):
return 1/np.sqrt(2*np.pi*d)*np.exp(-(x-u)**2/2/d**2)
x = np.linspace(-3, 3, 50)
y = nd(x)
plt.plot(x, y)
# 調整座標
ax = plt.gca()
ax.spines['right'].set_color('none')
ax.spines['top'].set_color('none')
ax.xaxis.set_ticks_position('bottom')
ax.yaxis.set_ticks_position('left')
ax.spines['bottom'].set_position(('data', 0))
ax.spines['left'].set_position(('data', 0))
plt.show()
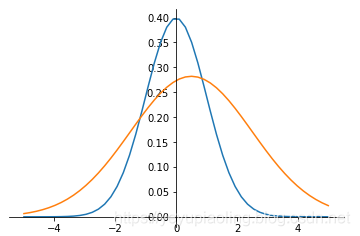
非標準正態分佈的標準化(Normalization)¶
- 將非標準正態變爲標準正態。
- 將每個數據減均值,除標準差。
\[y=\frac{x-\mu}{\sigma}\]
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
def nd(x, u=0, d=1):
return 1/np.sqrt(2*np.pi*d)*np.exp(-(x-u)**2/2/d**2)
x = np.linspace(-5, 5, 50)
y1 = nd(x)
y2 = nd(x, 0.5, 2)
plt.plot(x, y1)
plt.plot(x, y2)
# 調整座標
ax = plt.gca()
ax.spines['right'].set_color('none')
ax.spines['top'].set_color('none')
ax.xaxis.set_ticks_position('bottom')
ax.yaxis.set_ticks_position('left')
ax.spines['bottom'].set_position(('data', 0))
ax.spines['left'].set_position(('data', 0))
plt.show()
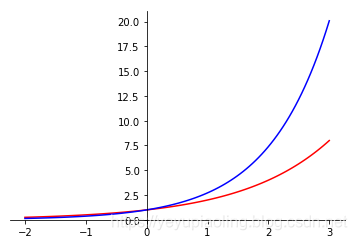
指數函數(Exponent)¶
- 常用2, e的指數函數;
- 輸入爲任意實數;
- 輸出爲非負數。
\[y_1=2^x$$
$$y_2=e^x\]
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
x = np.linspace(-2, 3, 100)
y1 = 2**x
y2 = np.exp(x)
plt.plot(x,y1, color='red')
plt.plot(x, y2, color='blue')
# 調整座標
ax = plt.gca()
ax.spines['right'].set_color('none')
ax.spines['top'].set_color('none')
ax.xaxis.set_ticks_position('bottom')
ax.yaxis.set_ticks_position('left')
ax.spines['bottom'].set_position(('data', 0))
ax.spines['left'].set_position(('data', 0))
plt.show()
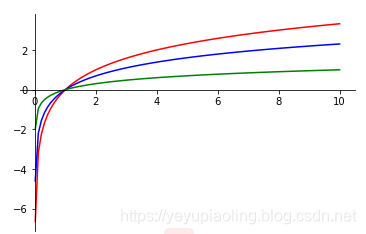
對數函數(Logarithm)¶
- 常用以2, e, 10爲底的對數函數;
- 定義域爲正數;
- 值域爲全體實數;
- 輸入在(0, 1)範圍內時,輸出爲負數。
\(\(y_1=log_2x\)\)
\(\(y_2=lnx\)\)
\(\(y_3=lgx\)\)
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
x = np.linspace(0.01, 10, 100)
y1 = np.log2(x)
y2 = np.log(x)
y3 = np.log10(x)
plt.plot(x, y1, color='red')
plt.plot(x, y2, color='blue')
plt.plot(x, y3, color='green')
# 調整座標
ax = plt.gca()
ax.spines['right'].set_color('none')
ax.spines['top'].set_color('none')
ax.xaxis.set_ticks_position('bottom')
ax.yaxis.set_ticks_position('left')
ax.spines['bottom'].set_position(('data', 0))
ax.spines['left'].set_position(('data', 0))
plt.show()
Softmax函數¶
- 在分類網絡的輸出層中作激活函數,輸出概率;
- 先通過指數函數,把所有輸出都變爲整數;
- 再做歸一化,每個數都除以所有數的和,輸出各分類的概率。
\[P_i=\frac{e^{x_i}}{\sum_{i=1}^Ne^{x_i}}\left(x:x_1,x_2,\ldots,x_N\right)\]
import numpy as np
x = np.array([-0.02964322, -0.11363636, 0.39417967, -0.06916996, 0.14260276])
print('原始輸出:', x)
prob = np.exp(x)/np.sum(np.exp(x))
print('概率輸出:', prob)
輸出:
原始輸出: [-0.02964322 -0.11363636 0.39417967 -0.06916996 0.14260276]
概率輸出: [0.17868493 0.16428964 0.27299323 0.17175986 0.21227234]
One-hot 編碼¶
- 在分類網絡中,用於對類別進行編碼;
- 編碼長度等於類別數;
- 每個編碼只有一位爲1,其餘都爲0;
- 所有編碼向量都正交。
示例:
假如有5類,則編碼爲:
第一類:[1, 0, 0, 0, 0]
第二類:[0, 1, 0, 0, 0]
第三類:[0, 0, 1, 0, 0]
第四類:[0, 0, 0, 1, 0]
第五類:[0, 0, 0, 0, 1]
交叉熵(Cross Entropy)¶
- 常用於分類問題中,做損失函數;
- 從分佈的角度,讓預測概率趨近於標籤。
\(Label:[l_1, l_2, \ldots, l_N]\) ——經過One-hot編碼
\(predict:[P_1, P_2, \ldots, P_N]\) ——經過Softmax函數
\[ce=-\sum_{i=1}^Nl_i\cdot\log^{P_i}\]
import numpy as np
# one-hot 編碼的標籤
label = np.array([0,0,1,0,0])
print('分類標籤:', label)
# 網絡實際輸出
x1 = np.array([-0.02964322, -0.11363636, 3.39417967, -0.06916996, 0.14260276])
x2 = np.array([-0.02964322, -0.11363636, 1.39417967, -0.06916996, 5.14260276])
print('網絡輸出1:', x1)
print('網絡輸出2:', x2)
# softmax 之後的模擬概率
p1 = np.exp(x1) / np.sum(np.exp(x1))
p2 = np.exp(x2) / np.sum(np.exp(x2))
print('概率輸出1:', p1)
print('概率輸出2:', p2)
# 交叉熵
ce1 = -np.sum(label * np.log(p1))
ce2 = -np.sum(label * np.log(p2))
print('交叉熵1:', ce1)
print('交叉熵2:', ce2)
輸出:
分類標籤: [0 0 1 0 0]
網絡輸出1: [-0.02964322 -0.11363636 3.39417967 -0.06916996 0.14260276]
網絡輸出2: [-0.02964322 -0.11363636 1.39417967 -0.06916996 5.14260276]
概率輸出1: [0.02877271 0.02645471 0.88293386 0.0276576 0.03418112]
概率輸出2: [0.00545423 0.00501482 0.02265122 0.00524284 0.96163688]
交叉熵1: 0.12450498821197674
交叉熵2: 3.787541448750617
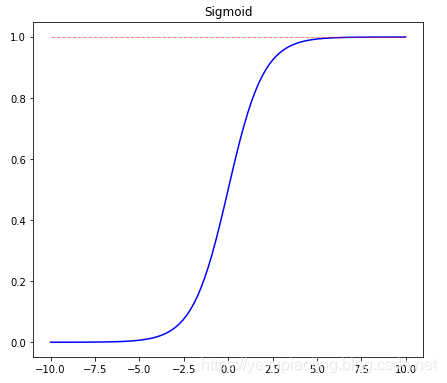
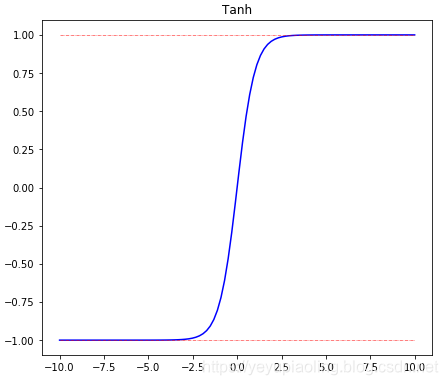
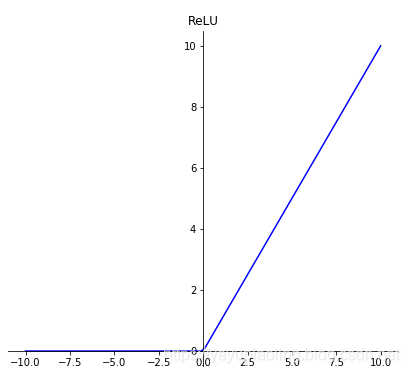
激活函數(Activation Function)¶
- 引入非線性因素,使模型有更強的表達能力;
- 輸出層採用softmax激活,可以模擬輸出概率;
- sigmoid和tanh都有飽和區,會導致梯度消失;
- 在深度學習中,sigmoid和tanh主要用於做各種門或開關;
- 在深度學習中,最常用的激活函數爲ReLU及其變體。
\[\delta(x)=\frac{1}{1+e^{-x}}$$
$$Tanh(x)=\frac{e^x-e^{-x}}{e^x+e^{-x}}$$
$$ReLU(x)=max(x, 0)\]
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
x = np.linspace(-10, 10, 100)
# plt.figure(31)
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 20))
# Sigmoid
sigmoid = 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
top = np.ones(100)
plt.subplot(311)
plt.plot(x, sigmoid, color='blue')
plt.plot(x, top, color='red', linestyle='-.', linewidth=0.5)
plt.title(s='Sigmoid')
# Tanh
tanh = (np.exp(x) - np.exp(-x)) / (np.exp(x) + np.exp(-x))
top = np.ones(100)
bottom = -np.ones(100)
plt.subplot(312)
plt.plot(x, tanh, color='blue')
plt.plot(x, top, color='red', linestyle='-.', linewidth=0.5)
plt.plot(x, bottom, color='red', linestyle='-.', linewidth=0.5)
plt.title('Tanh')
# ReLU
relu = np.maximum(x, 0)
plt.subplot(313)
plt.plot(x, relu, color='blue')
plt.title('ReLU')
# 調整座標
ax = plt.gca()
ax.spines['right'].set_color('none')
ax.spines['top'].set_color('none')
ax.xaxis.set_ticks_position('bottom')
ax.yaxis.set_ticks_position('left')
ax.spines['bottom'].set_position(('data', 0))
ax.spines['left'].set_position(('data', 0))
plt.show()
源代碼地址:https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/projectdetail/176057