# 目錄
@[toc]
前言¶
有時候我們需要一些網絡數據來工作、學習,比如我們做深度學習的。當做一個分類任務時,需要大量的圖像數據,這個圖像數據如果要人工一個個下載的,這很明顯不合理的,這是就要用到爬蟲程序。使用爬蟲程序幫我們下載所需要的圖像。那麼我們就開始學習爬蟲吧。
爬蟲的框架¶
整體框架¶
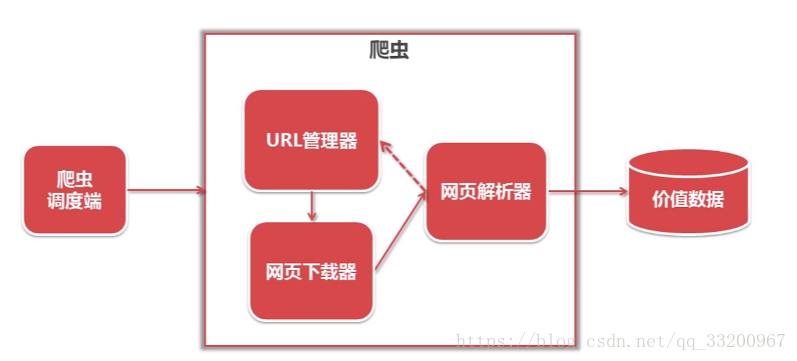
下圖是爬蟲的整體框架,其中包括調度端、URL管理器、網頁下載器、網頁解析器、價值數據,它們的作用如下:
調度端:主要是調用URL管理器、網頁下載器、網頁解析器,也設置爬蟲的入口;
URL管理器:管理要爬網頁的URL,添加新的URL,標記已爬過的URL,獲取要爬的URL;
網頁下載器:通過URL下載網頁數據,並以字符串保存;
網頁解析器:解析網頁下載器獲取到的字符串數據,獲取用戶需要的數據;
價值數據:所有有用的數據都存儲在這裏。
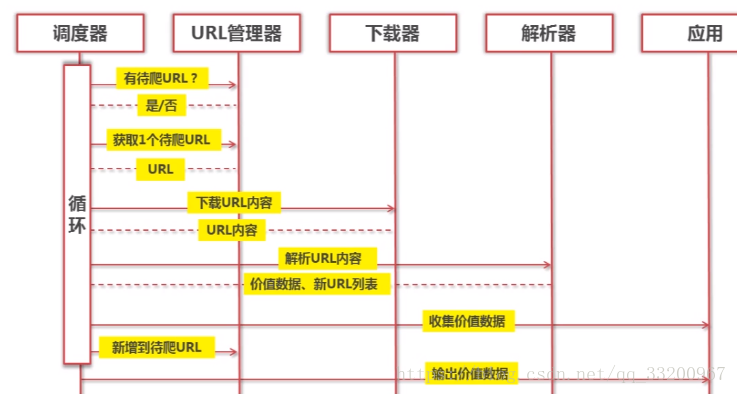
下圖是爬蟲的一個順序圖,從順序圖中可以看出調度器通過訓練調用URL管理器、網頁下載器、網頁解析器來不斷獲取網絡數據。
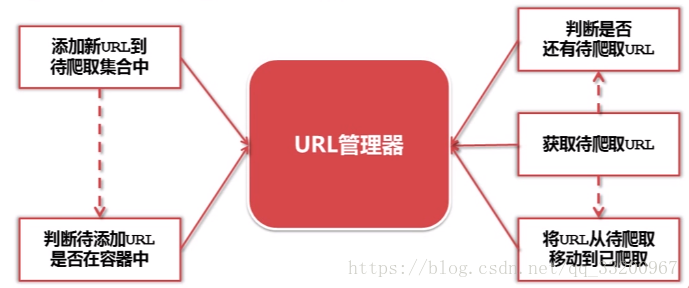
URL管理器¶
如圖所示,URL管理器是負責管理要爬取網頁的URL的。當有新的URL,就把新的URL添加到管理器中,在添加之前還有判斷URL是否已經存在。在獲取時,先判斷是否還有URL,如果有就提前URL並將它移動到已爬取的列表中。這樣保證不添加新的重複的URL
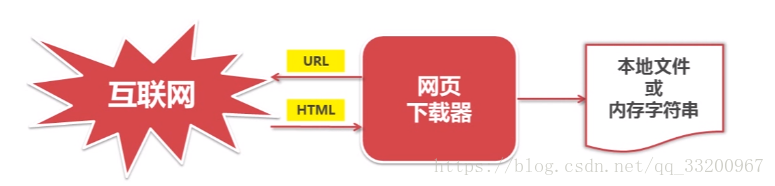
網頁下載器¶
從URL管理器中獲取的URL,我們要把這些URL的網頁數據下載下來,這是就要使用到了網頁下載器,這說到下載的有本地文件或字符串,這是因爲當我們爬取的是文件時,如圖片,下載的就是文件了。當我們爬取的是網頁中的內容數據時,這時就是字符串。
網頁下載器的代碼片段:
# coding=utf-8
import urllib2
url = "https://www.baidu.com"
response = urllib2.urlopen(url)
code = response.getcode()
content = response.read()
print "狀態碼:", code
print "網頁內容", content
還可以添加請求頭,模仿其他瀏覽器訪問
# coding=utf-8
import urllib2
url = "https://www.baidu.com"
request = urllib2.Request(url)
# 模仿火狐瀏覽器
request.add_header("user-agent", "Mozilla/5.0")
response = urllib2.urlopen(request)
code = response.getcode()
content = response.read()
print "狀態碼:", code
print "網頁內容", content
輸出信息爲:
狀態碼: 200
網頁內容 <html>
<head>
<script>
location.replace(location.href.replace("https://","http://"));
</script>
</head>
<body>
<noscript><meta http-equiv="refresh" content="0;url=http://www.baidu.com/"></noscript>
</body>
</html>
網頁解析器¶
在網頁下載器中下載的衆多字符串中,我們要提前我們需要的數據,如新的要爬取的URL、我們需要的網頁數據。通過這個網頁解析器就可以解析這些數據了。獲取新的URL可以添加到URL管理器中,獲取有用的數據就將它保存。
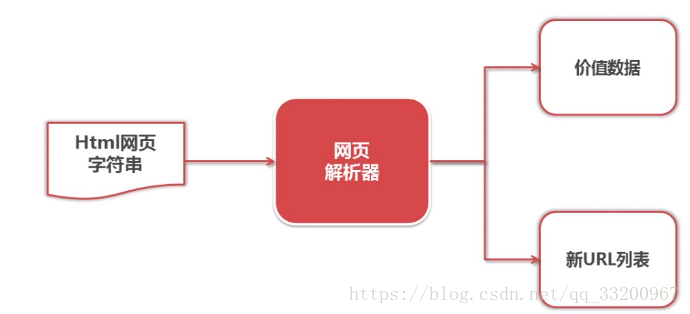
網頁解析器的代碼片段:
# coding=utf-8
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
html_doc = """
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
<body>
<p class="title"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p>
"""
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc, 'html.parser', from_encoding='utf-8')
# 尋找屬性class爲title的p標籤
title_all = soup.find('p', class_="title")
print title_all
# 獲取該標籤對應的內容
title = title_all.get_text()
print title
輸出信息如下:
<p class="title"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p>
The Dormouse's story
爬蟲程序¶
這個程序是爬取CSDN博客的文章,並爬取相關的文章。比如我們的爬蟲入口是一篇《把項目上傳到碼雲》的文章,在每章文章的最後都有相關的文章推薦,這些推薦的文章的URL就是我們補充的URL來源。如:
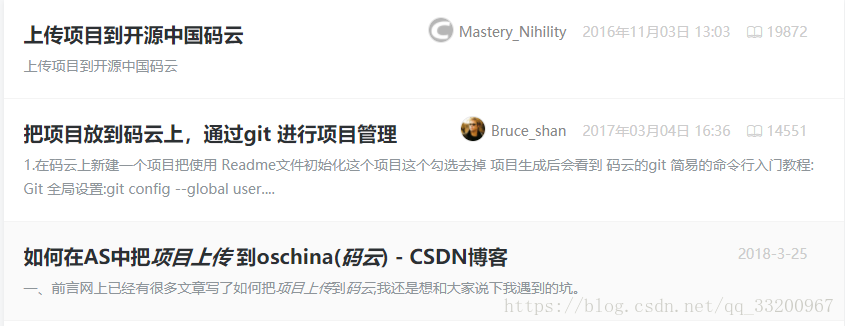
然後觀察整個文章的網頁源碼,可以得到文章的標題的代碼片段如下,關鍵定位信息是class="csdn_top":
<article>
<h1 class="csdn_top">把項目上傳到碼雲</h1>
<div class="article_bar clearfix">
<div class="artical_tag">
<span class="original">
原創 </span>
<span class="time">2017年04月15日 20:39:02</span>
</div>
文章內容的代碼片段如下,關鍵定位信息是class="article_content csdn-tracking-statistics tracking-click":
<div id="article_content" class="article_content csdn-tracking-statistics tracking-click" data-mod="popu_519" data-dsm="post">
<div class="markdown_views">
<p>一、爲什麼要使用碼雲而不使用GitHub?會有很多朋友這樣問,原因有以下幾條: <br>
推薦文章的代碼片段如下,關鍵定位信息是strategy="BlogCommendFromBaidu_0":
<div class="recommend_list clearfix" id="rasss">
<dl class="clearfix csdn-tracking-statistics recommend_article" data-mod="popu_387" data-poputype="feed" data-feed-show="false" data-dsm="post">
<a href="https://blog.csdn.net/Mastery_Nihility/article/details/53020481" target="_blank" strategy="BlogCommendFromBaidu_0">
<dd>
<h2>上傳項目到開源中國碼雲</h2>
<div class="summary">
上傳項目到開源中國碼雲
</div>
有了這些定位,就可以開始爬取數據了,我們開始吧。
調度器¶
創建一個spider_mamin.py文件來編寫調度器的代碼,這個就是調度中心,在這裏控制整個爬蟲程序:
# coding=utf-8
import html_downloader
import html_outputer
import html_parser
import url_manager
class SpiderMain(object):
# 調度程序
def __init__(self):
# 獲取URL管理器
self.urls = url_manager.UrlManager()
# 獲取網頁下載器
self.downloader = html_downloader.HtmlDownloader()
# 獲取網頁解析器
self.parser = html_parser.HtmlParser()
# 獲取數據輸出器
self.output = html_outputer.HtmlOutput()
def craw(self, root_url, max_count):
count = 1
# 添加爬蟲入口的跟路徑
self.urls.add_new_url(root_url)
# 創建一個循環,如果URL管理器中還有新的URL就一直循環
while self.urls.has_new_url():
try:
# 從URL管理器中獲取新的URL
new_url = self.urls.get_new_url()
print 'craw %d : %s ' % (count, new_url)
# 下載網頁
html_cont = self.downloader.downloader(new_url)
# 解析網頁數據
new_urls, new_data = self.parser.parser(new_url, html_cont)
# 添加新的URL
self.urls.add_new_urls(new_urls)
# 添加新的數據
self.output.collect_data(new_data)
# 滿足爬取數量及中斷
if count == max_count:
break
count = count + 1
except Exception, e:
print '爬取失敗:', e
# 輸出數據
self.output.output_html()
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 爬蟲的根URL
root_url = "https://blog.csdn.net/qq_33200967/article/details/70186759"
# 爬取的數量
max_count = 100
obj_spider = SpiderMain()
# 啓動調度器
obj_spider.craw(root_url, max_count)
URL管理器¶
創建一個url_manager.py文件編寫URL管理器的代碼,添加新的URL和提供URL給網頁下載器,由這個程序負責:
# coding=utf-8
class UrlManager(object):
# url管理器
def __init__(self):
self.new_urls = set()
self.old_urls = set()
# 向管理器中添加一個新的url
def add_new_url(self, url):
if url is None:
return
# 判斷要添加的URL是否已存在新列表或者舊列表中
if url not in self.new_urls and url not in self.old_urls:
self.new_urls.add(url)
# 向管理器中添加批量url
def add_new_urls(self, urls):
if urls is None or len(urls) == 0:
return
for url in urls:
# 添加新的URL
self.add_new_url(url)
# 判斷管理器中是否有新的待爬取的url
def has_new_url(self):
return len(self.new_urls) != 0
# 從url中獲取一個新的待爬取的url
def get_new_url(self):
# 獲取並移除最先添加的URL
new_url = self.new_urls.pop()
# 把這個路徑添加到已爬取的列表中
self.old_urls.add(new_url)
return new_url
網頁下載器¶
創建一個html_downloader.py文件來編寫網頁下載器的代碼,下載網頁的字符串數據,都是HTML的代碼:
# coding=utf-8
import urllib2
class HtmlDownloader(object):
# html下載器
def downloader(self, url):
# 如果路徑爲空就返回空
if url is None:
return None
# 打開網頁數據
response = urllib2.urlopen(url)
# 判斷是否訪問成功,如果不成功就返回空
if response.getcode() != 200:
return None
# 返回網頁數據
return response.read()
網頁解析器¶
創建一個html_parser.py文件來編寫網頁解析器的代碼,從網頁下載器獲取的HTML格式的字符串中解析想要的數據個URL:
# coding=utf-8
import re
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
class HtmlParser(object):
def parser(self, page_url, html_cont):
"""
# html解析器
:param page_url: 網頁的URL
:param html_cont: 網頁的字符串數據
:return: 網頁包含相關的URL和文章的內容
"""
# 判斷網頁URL和網頁內容是否爲空
if page_url is None or html_cont is None:
return
# 獲取解析器
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_cont, 'html.parser', from_encoding='utf-8')
# 獲取解析到的URL
new_urls = self._get_new_urls(soup)
# 獲取解析到的文章數據
new_data = self._get_new_data(page_url, soup)
return new_urls, new_data
# 解析相關文章的URL
def _get_new_urls(self, soup):
new_urls = set()
# 獲取相關的文章URL,格式如下:
# <a href="https://blog.csdn.net/qq_18601953/article/details/78395878"
# target="_blank" strategy="BlogCommendFromBaidu_7">
links = soup.find_all('a', strategy=re.compile(r"BlogCommendFromBaidu_\d+"))
# 提取所有相關的URL
for link in links:
new_url = link['href']
new_urls.add(new_url)
return new_urls
# 解析數據
def _get_new_data(self, page_url, soup):
res_data = {}
# 獲取URLurl
res_data['url'] = page_url
# 獲取標題<h1 class="csdn_top">把項目上傳到碼雲</h1>
essay_title = soup.find('h1', class_="csdn_top")
res_data['title'] = essay_title.get_text()
# 內容標籤的格式如下:
# <div id="article_content" class="article_content csdn-tracking-statistics tracking-click"
# data-mod="popu_519" data-dsm="post">
essay_content = soup.find('div', class_="article_content csdn-tracking-statistics tracking-click")
res_data['content'] = essay_content.get_text()
return res_data
數據存儲器¶
創建一個html_outputer.py文件來編寫存儲數據的代碼,當爬取完成數據之後,通過這個程序永久保存爬取的數據:
# coding=utf-8
class HtmlOutput(object):
#html輸出器
def __init__(self):
self.datas = []
#收集數據
def collect_data(self, data):
if data is None:
return
self.datas.append(data)
#將收集好的數據寫出到html文件中
def output_html(self):
fout = open('output.html','w')
fout.write("<html>")
fout.write("<body>")
fout.write("<table>")
if len(self.datas) == 0:
print "數據爲空!"
#ascii
for data in self.datas:
fout.write("<tr>")
fout.write("<td>%s</td>" % data['url'])
fout.write("<td>%s</td>" % data['title'].encode('utf-8'))
fout.write("<td>%s</td>" % data['content'].encode('utf-8'))
fout.write("</tr>")
fout.write("</table>")
fout.write("</body>")
fout.write("</html>")
fout.close()
運行代碼¶
運行調度器代碼spider_mamin.py,可以看到爬取過程輸出的日誌信息,如果出現失敗是正常的:
craw 1 : https://blog.csdn.net/qq_33200967/article/details/70186759
craw 2 : https://blog.csdn.net/qq_18601953/article/details/78395878
craw 3 : https://blog.csdn.net/wust_lh/article/details/68068176
爬取完成之後,所有的數據都會以HTML格式存儲在output.html中。可以在瀏覽器中打開,如:
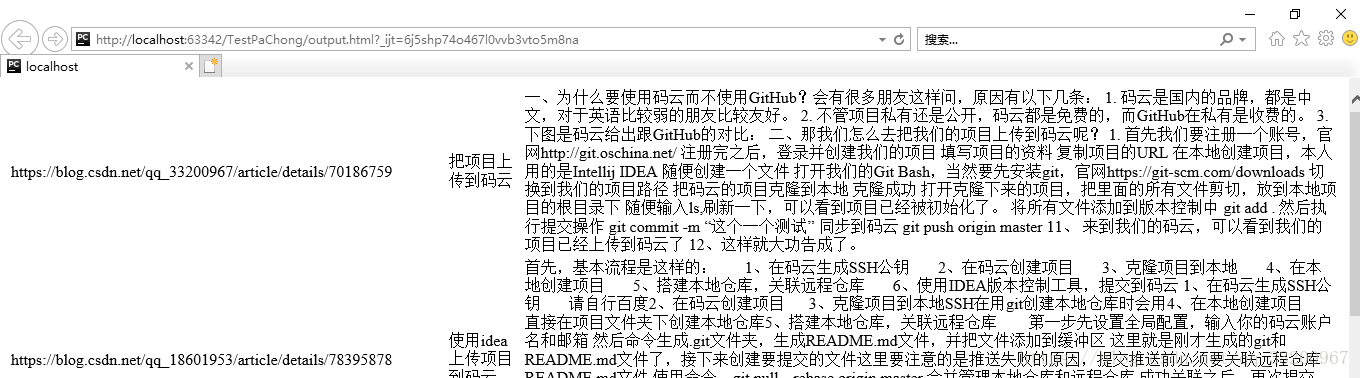
爲了讀者方便使用代碼,我已將這些代碼打包了,可以在這裏下載完整代碼。
參考資料¶
- http://www.imooc.com/learn/563