*This article is based on PaddlePaddle 0.13.0 and Python 2.7
Introduction¶
VisualDL is a visualization tool designed for deep learning tasks, including scalar, parameter distribution, model structure, and image visualization. It enables “what you see is what you get” functionality. With VisualDL, you can observe training processes, analyze models, and improve convergence.
The previous paddle.v2.plot interface only supported line charts for CSOT, while VisualDL offers more features:
1. scalar: Trend plots for training/test errors
2. image: Visualize images for convolutional layers or parameter analysis
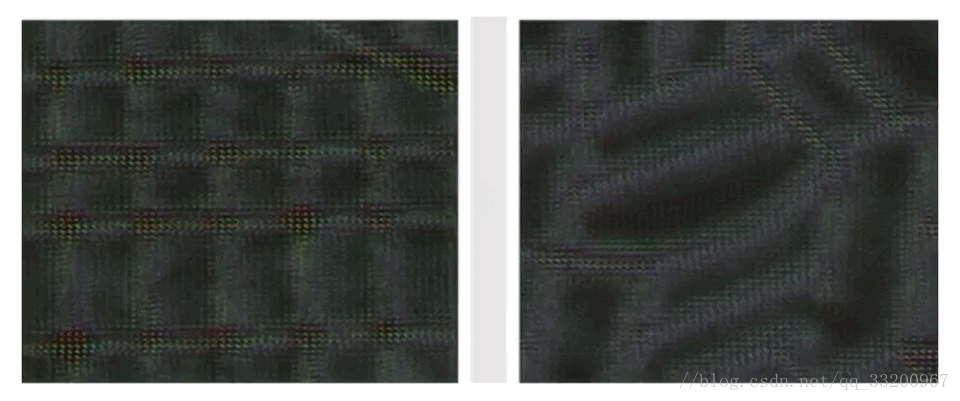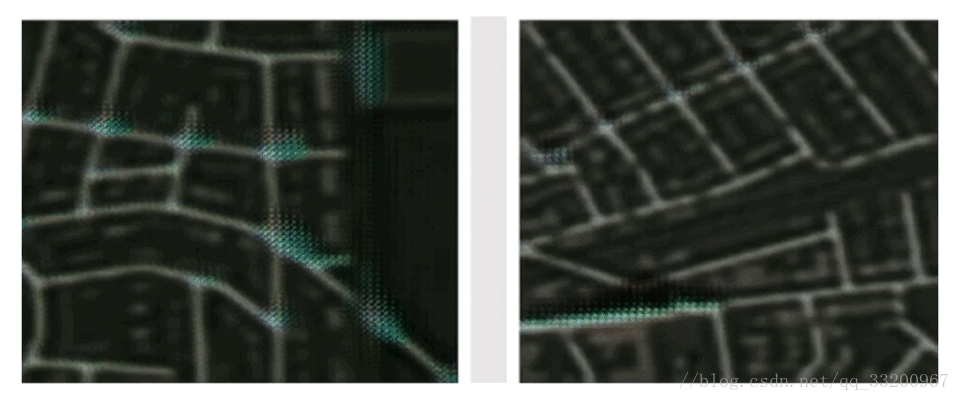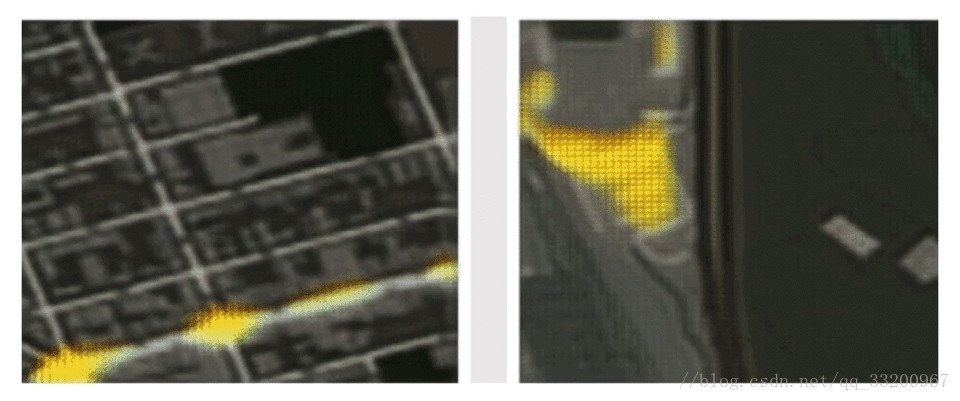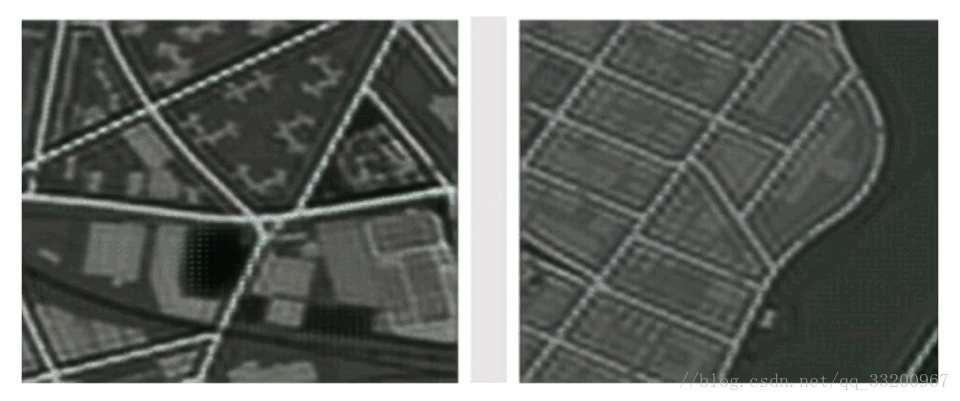
3. histogram: Show parameter distributions and trends
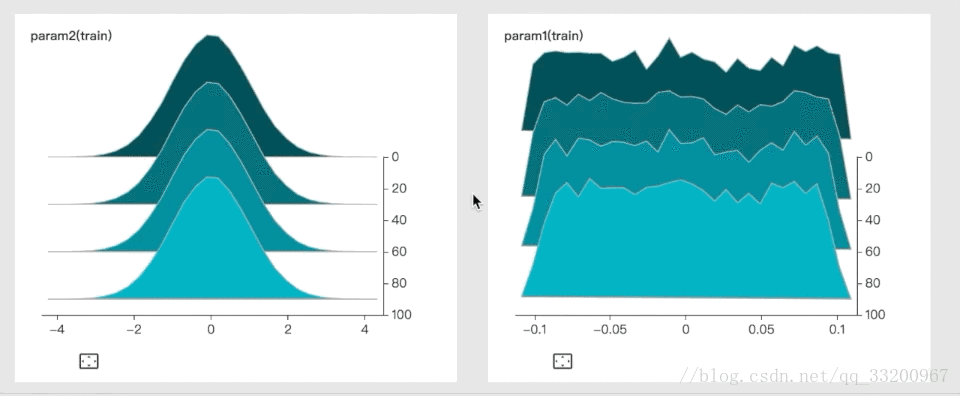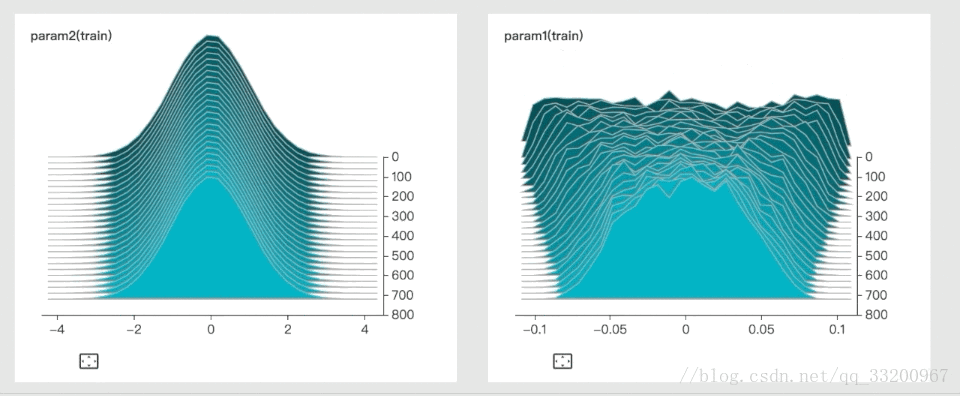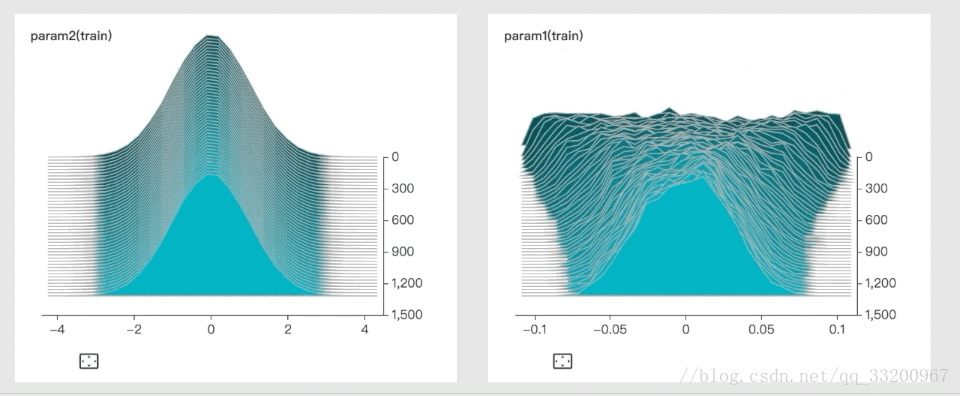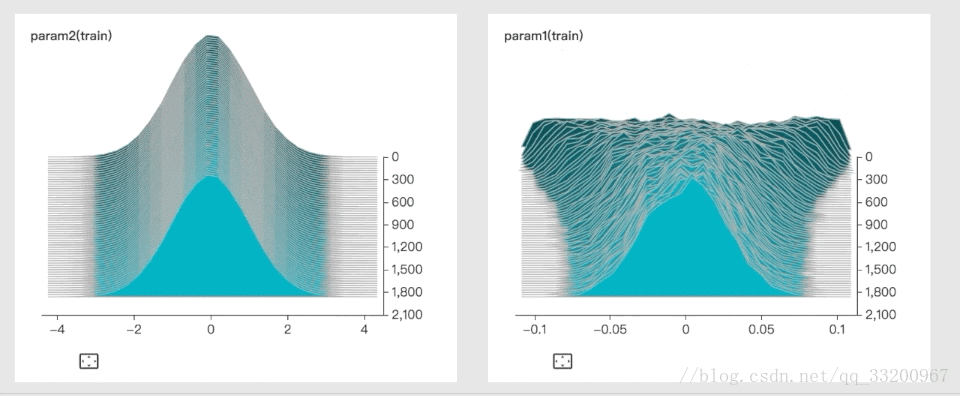
4. graph: Visualize model architecture
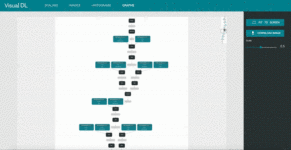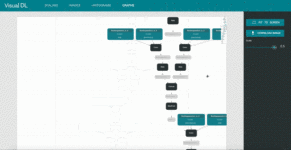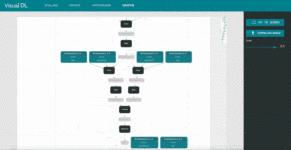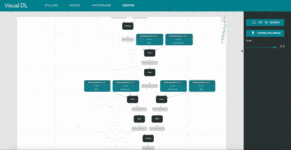
These images are from VisualDL’s GitHub.
VisualDL is written in C++ with both C++ and Python SDKs. We’ll use the Python SDK here. It supports major DNN frameworks including PaddlePaddle, PyTorch, and MXNet.
Installation of VisualDL¶
This chapter covers Ubuntu installation (Mac should be similar).
Installation via pip¶
Installation is simple with one command:
pip install --upgrade visualdl
Test installation by downloading a sample log:
# Download log
vdl_create_scratch_log
# If command not found, use:
vdl_scratch.py
Start VisualDL with the log:
visualdl --logdir ./scratch_log --port 8080
Parameters:
- host: Set IP address
- port: Set port number
- model_pb: Specify ONNX model file (not used here)
Note: If you encounter the error below, upgrade protobuf:
TypeError: __init__() got an unexpected keyword argument 'file'
pip install protobuf -U
Simple VisualDL Usage¶
Let’s test with a basic example:
# coding=utf-8
from visualdl import LogWriter
# Create LogWriter with data path and sync cycle
logw = LogWriter("./random_log", sync_cycle=10000)
# Create scalar plots for train/test
with logw.mode('train') as logger:
scalar0 = logger.scalar("scratch/scalar")
with logw.mode('test') as logger:
scalar1 = logger.scalar("scratch/scalar")
# Add data records
for step in range(1000):
scalar0.add_record(step, step * 1. / 1000)
scalar1.add_record(step, 1. - step * 1. / 1000)
Run the script, then start VisualDL:
visualdl --logdir ./random_log --port 8080
Access http://127.0.0.1:8080 to view results.
Using VisualDL in PaddlePaddle¶
Define VisualDL Components¶
Create three components: scalar, image, histogram:
logdir = "../data/tmp"
logwriter = LogWriter(logdir, sync_cycle=10)
# Loss trend plot
with logwriter.mode("train") as writer:
loss_scalar = writer.scalar("loss")
# Accuracy trend plot
with logwriter.mode("train") as writer:
acc_scalar = writer.scalar("acc")
# Image visualization (conv and input)
with logwriter.mode("train") as writer:
conv_image = writer.image("conv_image", num_samples, 1)
input_image = writer.image("input_image", num_samples, 1)
# Parameter distribution histogram
with logwriter.mode("train") as writer:
param1_histgram = writer.histogram("param1", 100)
PaddlePaddle Code¶
Define data, model, and training loop:
# Image dimensions
class_dim = 10
image_shape = [3, 32, 32]
# Input data
image = fluid.layers.data(name='image', shape=image_shape, dtype='float32')
label = fluid.layers.data(name='label', shape=[1], dtype='int64')
# Model definition
net, conv1 = vgg16_bn_drop(image)
predict = fluid.layers.fc(
input=net,
size=class_dim,
act='softmax',
param_attr=ParamAttr(name="param1", initializer=NormalInitializer()))
# Loss and accuracy
cost = fluid.layers.cross_entropy(input=predict, label=label)
avg_cost = fluid.layers.mean(x=cost)
batch_acc = fluid.layers.accuracy(input=predict, label=label)
# Optimizer
optimizer = fluid.optimizer.Momentum(
learning_rate=learning_rate,
momentum=0.9,
regularization=fluid.regularizer.L2Decay(5 * 1e-5))
opts = optimizer.minimize(avg_cost)
# Execution setup
place = fluid.CUDAPlace(0) if use_cuda else fluid.CPUPlace()
exe = fluid.Executor(place)
exe.run(fluid.default_startup_program())
# Data loader
train_reader = paddle.batch(
paddle.dataset.cifar.train10(), batch_size=BATCH_SIZE)
feeder = fluid.DataFeeder(place=place, feed_list=[image, label])
# Training loop
step = 0
for pass_id in range(num_passes):
accuracy.reset()
for batch_id, data in enumerate(train_reader()):
loss, conv1_out, param1, acc, weight = exe.run(
fluid.default_main_program(),
feed=feeder.feed(data),
fetch_list=[avg_cost, conv1, param1_var, batch_acc, batch_size])
accuracy.add(value=acc, weight=weight)
pass_acc = accuracy.eval()
Add Data to VisualDL¶
Log metrics and parameters:
# Image visualization
if sample_num == 0:
input_image.start_sampling()
conv_image.start_sampling()
idx = input_image.is_sample_taken()
if idx != -1:
input_image_data = np.transpose(image_data.reshape(image_shape), axes=[1, 2, 0])
input_image.set_sample(idx, input_image_data.shape, input_image_data.flatten())
conv_image_data = conv1_out[0][0]
conv_image.set_sample(idx, conv_image_data.shape, conv_image_data.flatten())
sample_num += 1
# Scalar metrics
loss_scalar.add_record(step, loss)
acc_scalar.add_record(step, acc)
# Histogram
param1_histgram.add_record(step, param1.flatten())
Running the Project¶
After training, start VisualDL:
visualdl --logdir ./tmp --port 8080
Access http://127.0.0.1:8080 to view:
1. Loss/accuracy trends
2. Convolutional layer visualization
3. Parameter distribution histograms
Project Code¶
GitHub: https://github.com/yeyupiaoling/LearnPaddle
References¶
- http://paddlepaddle.org/
- https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/VisualDL