Introduction¶
This project uses the EcapaTdnn model to implement voiceprint recognition. More models may be supported in the future. The project also supports various data preprocessing methods. The loss function references the approach used in face recognition projects PaddlePaddle-MobileFaceNets and uses ArcFace Loss. ArcFace Loss: Additive Angular Margin Loss, which normalizes feature vectors and weights, and adds an angular margin m to the angle θ. The angular margin has a more direct impact on the angle compared to the cosine margin.
Source Code Address: VoiceprintRecognition-PaddlePaddle (V1)
Environment Requirements:
- Python 3.7
- PaddlePaddle 2.2.2
Model Download¶
| Model | Preprocessing Method | Dataset | Number of Classes | Classification Accuracy | Pairwise Comparison Accuracy | Model Download Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EcapaTdnn | melspectrogram | Chinese Speech Corpus | 3242 | 0.9608 | 0.99980 | Download |
| EcapaTdnn | spectrogram | Chinese Speech Corpus | 3242 | 0.9617 | 0.99980 | Download |
| EcapaTdnn | melspectrogram | Larger Dataset | 6355 | 0.9109 | 0.99990 | Download |
| EcapaTdnn | spectrogram | Larger Dataset | 6355 | 0.9105 | 0.99990 | Download |
| EcapaTdnn | melspectrogram | Ultra-Large Dataset | 13718 | 0.9337 | 0.99995 | Download |
| EcapaTdnn | spectrogram | Ultra-Large Dataset | 13718 | 0.9326 | 0.99995 | Download |
Environment Installation¶
- Install the GPU version of PaddlePaddle. If already installed, no need to reinstall.
pip install paddlepaddle-gpu==2.2.2 -i https://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple/
- Install other dependent libraries using the following command. Note that the version of librosa must be 0.9.1, as older versions use a different method for calculating mel spectrograms.
pip install -r requirements.txt -i https://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple/
Note: Solutions for Installation Errors of librosa and pyaudio
Data Preparation¶
This tutorial uses the Chinese Speech Corpus, which contains voice data from 3242 speakers and over 1,130,000 voice samples. Please fully decompress the dataset before downloading. If you have other better datasets, you can mix them, but it is recommended to use the Python tool module audioread to process audio, denoise, and remove silent segments.
First, create a data list with the format <audio_file_path\t speaker_label>. This list is created for easy reading and compatibility with other voice datasets. The speaker label is the unique ID of the speaker. For different datasets, you can write a corresponding function to generate the data list and include all datasets in one file.
Write the following code in create_data.py. Since the Chinese Speech Corpus uses MP3 format, which was found to be slow to read, the author converted all MP3 audio files to WAV format. After creating the data list, check for incorrect data and remove it. Run the program to complete data preparation:
python create_data.py
After running the program, the generated data list will have the following format. For custom data, refer to this format: the first part is the relative path to the audio, and the second part is the corresponding speaker label (similar to classification).
dataset/zhvoice/zhmagicdata/5_895/5_895_20170614203758.wav 3238
dataset/zhvoice/zhmagicdata/5_895/5_895_20170614214007.wav 3238
dataset/zhvoice/zhmagicdata/5_941/5_941_20170613151344.wav 3239
dataset/zhvoice/zhmagicdata/5_941/5_941_20170614221329.wav 3239
dataset/zhvoice/zhmagicdata/5_941/5_941_20170616153308.wav 3239
dataset/zhvoice/zhmagicdata/5_968/5_968_20170614162657.wav 3240
dataset/zhvoice/zhmagicdata/5_968/5_968_20170622194003.wav 3240
dataset/zhvoice/zhmagicdata/5_968/5_968_20170707200554.wav 3240
dataset/zhvoice/zhmagicdata/5_970/5_970_20170616000122.wav 3241
Model Training¶
Use train.py to train the model. The project supports multiple audio preprocessing methods, specified via the parameter feature_method (options: melspectrogram for mel spectrogram, spectrogram for spectrogram). The data augmentation method is specified via the parameter augment_conf_path. During training, training logs are saved using VisualDL, which can be viewed at any time by starting VisualDL with the command visualdl --logdir=log --host 0.0.0.0.
# Single-card training
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python train.py
# Multi-card training
python -m paddle.distributed.launch --gpus '0,1' train.py
Sample training output logs:
----------- Configuration Arguments -----------
augment_conf_path: configs/augment.yml
batch_size: 64
feature_method: melspectrogram
learning_rate: 0.001
num_epoch: 30
num_speakers: 3242
num_workers: 4
pretrained_model: None
resume: None
save_model_dir: models/
test_list_path: dataset/test_list.txt
train_list_path: dataset/train_list.txt
use_model: ecapa_tdnn
------------------------------------------------
I0424 08:57:03.707505 3377 nccl_context.cc:74] init nccl context nranks: 2 local rank: 0 gpu id: 0 ring id: 0
W0424 08:57:03.930370 3377 device_context.cc:447] Please NOTE: device: 0, GPU Compute Capability: 7.5, Driver API Version: 11.6, Runtime API Version: 10.2
W0424 08:57:03.932493 3377 device_context.cc:465] device: 0, cuDNN Version: 7.6.
I0424 08:57:05.431638 3377 nccl_context.cc:107] init nccl context nranks: 2 local rank: 0 gpu id: 0 ring id: 10
······
[2022-04-24 09:25:10.481272] Train epoch [0/30], batch: [7500/8290], loss: 9.03724, accuracy: 0.33252, lr: 0.00100000, eta: 14:58:26
[2022-04-24 09:25:32.909873] Train epoch [0/30], batch: [7600/8290], loss: 9.00004, accuracy: 0.33600, lr: 0.00100000, eta: 15:09:07
[2022-04-24 09:25:55.321806] Train epoch [0/30], batch: [7700/8290], loss: 8.96284, accuracy: 0.33950, lr: 0.00100000, eta: 15:13:13
[2022-04-24 09:26:17.836304] Train epoch [0/30], batch: [7800/8290], loss: 8.92626, accuracy: 0.34294, lr: 0.00100000, eta: 14:57:15
[2022-04-24 09:26:40.306800] Train epoch [0/30], batch: [7900/8290], loss: 8.88968, accuracy: 0.34638, lr: 0.00100000, eta: 14:51:06
[2022-04-24 09:27:02.778450] Train epoch [0/30], batch: [8000/8290], loss: 8.85430, accuracy: 0.34964, lr: 0.00100000, eta: 15:00:36
[2022-04-24 09:27:25.240278] Train epoch [0/30], batch: [8100/8290], loss: 8.81858, accuracy: 0.35294, lr: 0.00100000, eta: 14:51:58
[2022-04-24 09:27:47.690570] Train epoch [0/30], batch: [8200/8290], loss: 8.78368, accuracy: 0.35630, lr: 0.00100000, eta: 14:55:41
======================================================================
[2022-04-24 09:28:12.084404] Test 0, accuracy: 0.76057 time: 0:00:04
======================================================================
[2022-04-24 09:28:12.909394] Train epoch [1/30], batch: [0/8290], loss: 5.83753, accuracy: 0.68750, lr: 0.00099453, eta: 2 days, 3:47:48
[2022-04-24 09:28:35.346418] Train epoch [1/30], batch: [100/8290], loss: 5.80430, accuracy: 0.64527, lr: 0.00099453, eta: 15:00:01
[2022-04-24 09:28:57.873686] Train epoch [1/30], batch: [200/8290], loss: 5.78946, accuracy: 0.64218, lr: 0.00099453, eta: 14:46:39
······
VisualDL Page:
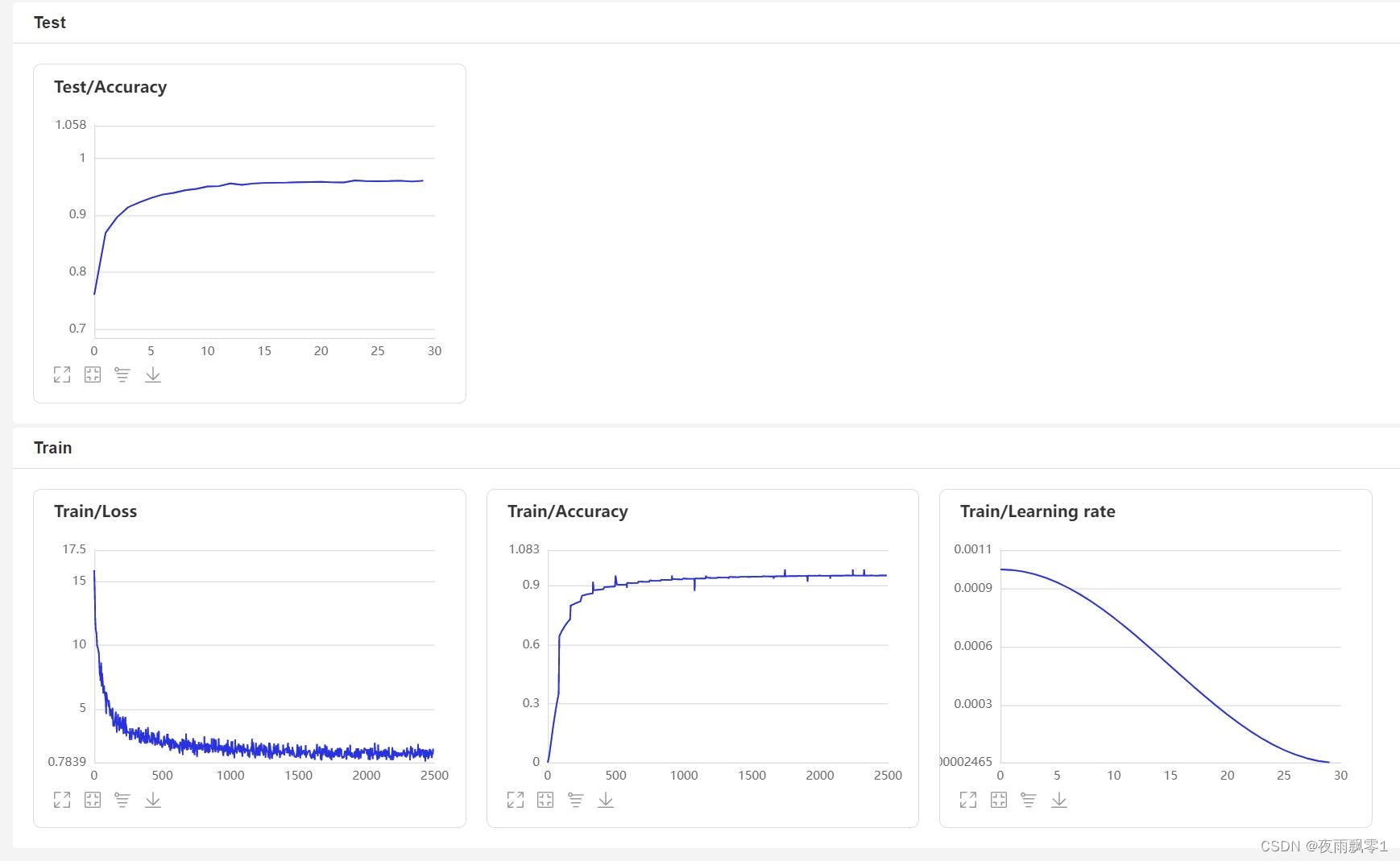
Data Augmentation¶
This project provides several audio augmentation operations: random cropping, adding background noise, adjusting speech rate, adjusting volume, and SpecAugment. The parameters for the latter four can be modified in configs/augment.yml. The prob parameter specifies the probability of applying each augmentation operation; set it to 0 to disable the operation. For background noise addition, multiple noise audio files must be placed in dataset/noise; otherwise, the noise augmentation will be skipped.
noise:
min_snr_dB: 10
max_snr_dB: 30
noise_path: "dataset/noise"
prob: 0.5
Model Evaluation¶
After training, the model will save the prediction model. Use this model to predict the audio features in the test set, then perform pairwise comparisons using these features. The threshold ranges from 0 to 1 with a step size of 0.01 to find the optimal threshold and calculate the accuracy.
python eval.py
Sample evaluation output:
----------- Configuration Arguments -----------
feature_method: melspectrogram
list_path: dataset/test_list.txt
num_speakers: 3242
resume: models/
use_model: ecapa_tdnn
------------------------------------------------
W0425 08:27:32.057426 17654 device_context.cc:447] Please NOTE: device: 0, GPU Compute Capability: 7.5, Driver API Version: 11.6, Runtime API Version: 10.2
W0425 08:27:32.065165 17654 device_context.cc:465] device: 0, cuDNN Version: 7.6.
Successfully loaded model parameters and optimization method parameters: models/ecapa_tdnn/model.pdparams
Start extracting all audio features...
167it [00:15, 10.70it/s]
Classification accuracy: 0.9608
Start pairwise comparison of audio features...
100%|███████████████████████████| 5332/5332 [00:05<00:00, 1027.83it/s]
Finding the optimal threshold and corresponding accuracy...
100%|███████████████████████████| 100/100 [00:06<00:00, 16.54it/s]
The maximum pairwise comparison accuracy is achieved at a threshold of 0.58, with an accuracy of: 0.99980
Voiceprint Comparison¶
To implement voiceprint comparison, create infer_contrast.py and write the infer() function. The model outputs two values: the first is the classification output, and the second is the audio feature output. Here, we need to output the audio feature values, which are used for voiceprint recognition. Input two audio files, obtain their feature data via the prediction function, and compute the diagonal cosine value to measure similarity. The similarity threshold threshold can be adjusted based on project accuracy requirements.
python infer_contrast.py --audio_path1=audio/a_1.wav --audio_path2=audio/b_2.wav
Sample output:
```
----------- Configuration Arguments -----------
audio_path