Introduction¶
This project is PP-YOLOE implemented based on PaddleDetection. PP-YOLOE is a single-stage Anchor-free model. Its accuracy (COCO dataset mAP) and inference speed are both superior to the YOLOv5 model. PP-YOLOE achieves an accuracy of 49.0% on the COCO test-dev2017 dataset. The FP32 inference speed on a single V100 card is 123.4 FPS, and with TensorRT enabled on V100, the FP16 inference speed reaches 208.3 FPS. It includes four model types: X/L/M/S, suitable for deployment on various hardware, and the inference speed is extremely fast even when deployed on mobile phones.
Source Code Address: https://github.com/yeyupiaoling/PP-YOLOE
Model Table¶
This table is the official test table.
| Model Type | Epoch | Input Size | Box APval 0.5:0.95 |
Box APtest 0.5:0.95 |
Params(M) | FLOPs(G) | V100 FP32(FPS) | V100 TensorRT FP16(FPS) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S | 80 | 640 | 43.7 | 43.9 | 7.93 | 17.36 | 208.3 | 333.3 |
| M | 80 | 640 | 49.8 | 50.0 | 23.43 | 49.91 | 123.4 | 208.3 |
| L | 80 | 640 | 52.9 | 53.3 | 52.20 | 110.07 | 78.1 | 149.2 |
| X | 80 | 640 | 54.7 | 54.9 | 98.42 | 206.59 | 45.0 | 95.2 |
Installation Environment¶
- Install PaddlePaddle GPU version
conda install paddlepaddle-gpu==2.3.1 cudatoolkit=10.2 --channel https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/cloud/Paddle/
- Other dependent libraries
python -m pip install -r requirements.txt -i https://mirror.baidu.com/pypi/simple
Quick Usage¶
The following methods can be used to quickly export the COCO-trained prediction model from this project and use this prediction model for fast image inference.
- First, export the COCO prediction model. When the
--resume_modelparameter is None, it will automatically load the official COCO pre-trained model and export the prediction model using this pre-trained model.
python export_model.py --resume_model=None
- Then execute
infer.pyand specify the image path to perform inference.
python infer.py --image_path=dataset/test.jpg
Recognition result:

Training Model¶
Data Preparation¶
Prepare the training data train.json and evaluation data eval.json. This project only supports COCO-format datasets. If you use a VOC-format dataset, you can use the tools provided in the project for conversion. The usage is as follows. If your data is already in COCO format, you can skip this step.
- First, generate the VOC data list and label list. Execute the following command to generate the training data list
train.txt, evaluation data listeval.txt, and list filelabel_list.txt, which are all stored in thedatasetdirectory.
python create_voc_list.py
- Then execute
voc2coco.pyto generate a COCO-format dataset. The training data and evaluation data correspond totrain.jsonandeval.json, which are also stored in thedatasetdirectory.
python voc2coco.py
Training the Model¶
After preparing the data, you can start training. The training program should pay attention to the following important parameters: first, the model type model_type (there are four types: X/L/M/S), and second, the number of classes num_classes. These two parameters need to be set according to your actual situation. For more parameters, you can check the program file or execute python train.py -h. This project supports multi-card training, as shown in the following commands.
# Single-card training
python train.py --model_type=M --num_classes=80
# Multi-card training on a single machine
python -m paddle.distributed.launch --gpus '0,1' train.py --model_type=M --num_classes=80
Evaluating the Model¶
After training, if you need to check the accuracy of the model, you can execute the evaluation program eval.py, specifying the model type, number of classes, and the folder path of the model.
python eval.py --model_type=M --num_classes=80 --resume_model=output/PPYOLOE_M/best_model
Exporting the Prediction Model¶
After training, you can export the prediction model for subsequent deployment. Use the following command to complete the export of the prediction model. You need to specify the model type, number of classes, and the folder path of the model. image_shape specifies the size of the input image. If performance requirements are high, you can try setting a smaller image size, such as 3,416,416 or 3,320,320. The default is 3,640,640.
python export_model.py --model_type=M --num_classes=80 --resume_model=output/PPYOLOE_M/best_model
Prediction¶
This project provides three prediction methods: the first is using PaddlePaddle’s own Inference prediction interface, the second is using the ONNX prediction interface for inference, and the third is deploying on Android devices for prediction.
Inference¶
Using PaddlePaddle’s own Inference prediction interface for prediction, there are two ways here: the first is to use the image path for prediction and display the results, and the second is to use the camera or video file for prediction.
# Use image path for prediction and display results
python infer.py --image_path=dataset/test.jpg --model_dir=output_inference/PPYOLOE_M
# Use camera for real-time prediction
python infer_camera.py --device_id=0 --model_dir=output_inference/PPYOLOE_M
Recognition result:

ONNX¶
To use the ONNX prediction interface for inference, you need to additionally install the onnxruntime library. And you need to export the corresponding model using the following command. You need to modify the model path model_dir according to your actual situation.
python to_onnx_model.py
After exporting the ONNX model, you can use onnxruntime for inference. The command is as follows, specifying the prediction image path and the ONNX model path respectively. Execute the inference and display the results.
python infer_onnx.py --image_path=dataset/test.jpg --onnx_model=output_inference/model.onnx
Recognition result:

Android¶
If you want to deploy it on Android, you need to export the Paddle Lite model. The above command can export the Paddle Lite model. You need to modify the model path according to your actual situation and whether quantization is required. Quantization can reduce the model size by half, but there will be no significant change in prediction speed and generally will not reduce the model accuracy.
python to_lite_model.py
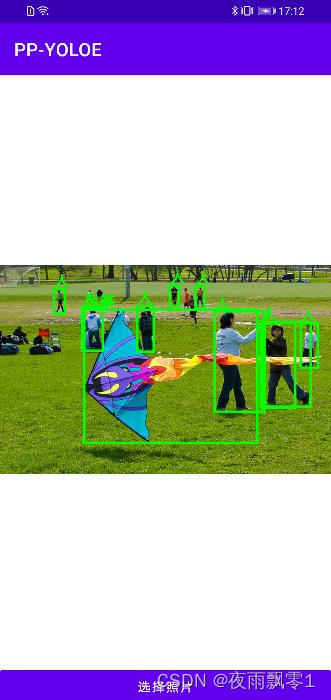
Using the Android Application: The Android source code is stored in the Android directory at the root of the project. You can directly open it with Android Studio. This demo application has two functions: “Open Camera Recognition” and “Open Album Recognition”. To replace the model you trained, you only need to operate the following two files:
- Replace the model file
detect_model.nbinAndroid/ai/src/main/assets/with your exporteddetect_model.nb. - Replace the label list file
label_list.txtinAndroid/ai/src/main/assets/with your list file, which is located indataset/label_list.txt.
Demo interface for opening album recognition:
References¶
- https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleDetection
- https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle-Lite