Foreword¶
Today, I’ll share a tutorial on using PaddlePaddle to train and predict with the PyramidBox model for large-scale face detection. Based on the open-source PyramidBox, this tutorial has been modified for easier training and prediction. Despite its large size, this model accurately detects faces even in crowded scenes with significant occlusion.
Tutorial Source Code: https://download.csdn.net/download/qq_33200967/14029049
PyramidBox is a single-stage face detector based on SSD, leveraging contextual information to tackle challenging face detection tasks. As shown in the figure below, it performs predictions across six scales of feature maps. Key modules include: LFPN, Pyramid Anchors, CPM, and Data-anchor-sampling.
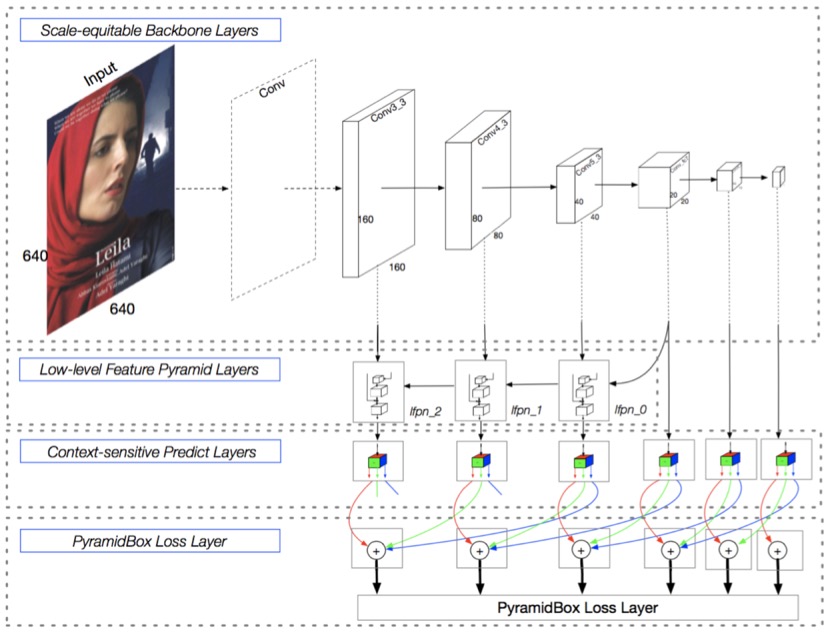
LFPN (Low-level Feature Pyramid Networks): Integrates high-level features (with rich context) and low-level features (with fine texture details). High-level features detect large faces, while low-level features detect small faces. A top-down fusion from intermediate layers constructs this low-level FPN for high-resolution integration.
Pyramid Anchors: Uses semi-supervised labeling to generate semantic anchor boxes. It introduces context-aware anchor sampling, expanding labeled faces by 1/2 in all directions (head labels) and customizing expansion for body labels to enhance training data diversity.
CPM (Context-sensitive Predict Module): Enhances the prediction network’s expressiveness with a context-aware structure.
Data-anchor-sampling: A novel sampling method that increases training diversity across scales, focusing on smaller faces by reweighting sample distribution.
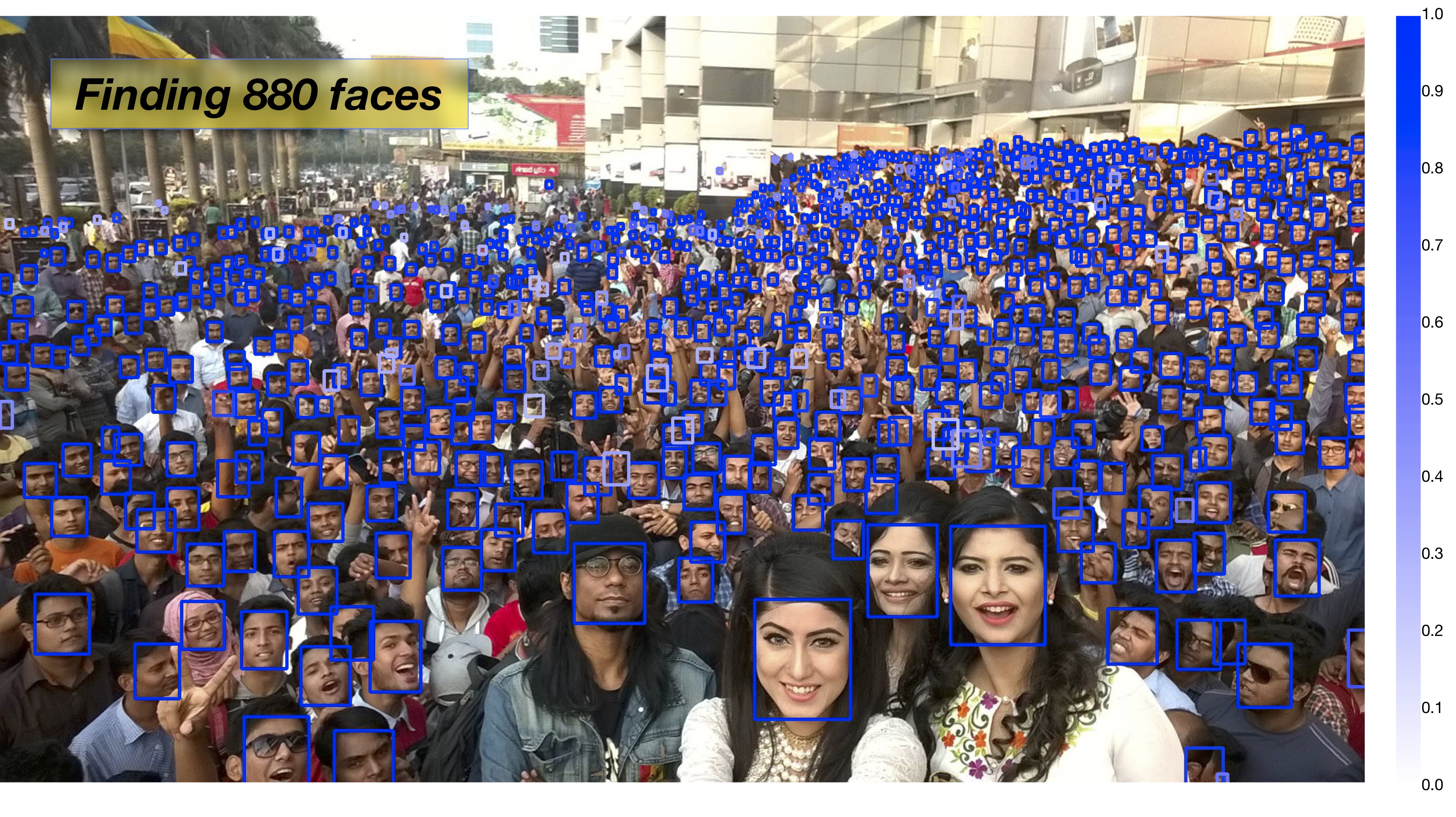
The following image demonstrates PyramidBox’s performance in detecting faces in crowded scenes. Whether you believe it or not, I do!

Training¶
- Download Dataset
Download and extract the following files into thedatadirectory:
https://share.weiyun.com/5WjCBWV
https://share.weiyun.com/5ot9Qv1
https://share.weiyun.com/5vSUomP
http://mmlab.ie.cuhk.edu.hk/projects/WIDERFace/support/bbx_annotation/wider_face_split.zip
Expected directory structure after extraction:
data
|-- download.sh
|-- wider_face_split
| |-- readme.txt
| |-- wider_face_train_bbx_gt.txt
| |-- wider_face_val_bbx_gt.txt
| `-- ...
|-- WIDER_train
| `-- images
| |-- 0--Parade
| ...
| `-- 9--Press_Conference
`-- WIDER_val
`-- images
|-- 0--Parade
...
`-- 9--Press_Conference
- Download Pretrained Model
Download the VGG pretrained model:
http://paddlemodels.bj.bcebos.com/vgg_ilsvrc_16_fc_reduced.tar.gz
Extract and place it in the project root directory.
- Start Training
Executetrain.pydirectly. For large models with insufficient GPU memory, reducebatch_size.
- Multi-GPU Support: Setexport CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1,2,3andnum_devicesto specify GPUs.
- Windows Users: Disable multiprocessing by settinguse_multiprocess=False(PaddlePaddle lacks multi-thread support on Windows).
Trained models are saved in the output directory.
Prediction¶
- Convert Pretrained Model to Inference Model
Official PyramidBox model download: http://paddlemodels.bj.bcebos.com/PyramidBox_WiderFace.tar.gz
Use the following code to convert parameters to inference format:
import paddle.fluid as fluid
from pyramidbox import PyramidBox
use_gpu = True
model_dir = 'PyramidBox_WiderFace'
save_infer_model_path = 'pyramidbox_model'
place = fluid.CUDAPlace(0) if use_gpu else fluid.CPUPlace()
exe = fluid.Executor(place)
main_program = fluid.Program()
startup_program = fluid.Program()
image_shape = [3, 1024, 1024]
with fluid.program_guard(main_program, startup_program):
network = PyramidBox(
data_shape=image_shape,
sub_network=True,
is_infer=True)
infer_program, nmsed_out = network.infer(main_program)
fetches = [nmsed_out]
fluid.io.load_persistables(exe, model_dir, main_program=infer_program)
fluid.io.save_inference_model(
save_infer_model_path,
['image'], [nmsed_out],
exe, main_program=infer_program,
model_filename='model', params_filename='params')
- Inference Code
Use the following code to load the inference model and detect faces:
import time
import cv2
import numpy as np
import paddle.fluid as fluid
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw
use_gpu = True
save_path = 'pyramidbox_model/'
[infer_program, feeded_var_names, target_var] = fluid.io.load_inference_model(
dirname=save_path,
executor=fluid.CUDAPlace(0) if use_gpu else fluid.CPUPlace(),
model_filename='model',
params_filename='params')
def get_shrink(height, width):
max_shrink_v1 = (0x7fffffff / 577.0 / (height * width)) ** 0.5
max_shrink_v2 = ((678 * 1024 * 2.0 * 2.0) / (height * width)) ** 0.5
max_shrink = min(max_shrink_v1, max_shrink_v2) - 0.3
max_shrink = max_shrink - (0.1 if 1.5 <= max_shrink < 2 else
0.2 if 2 <= max_shrink < 3 else
0.3 if 3 <= max_shrink < 4 else
0.4 if 4 <= max_shrink < 5 else 0.5)
return max(max_shrink, 1) if max_shrink < 1 else 1, max_shrink
def draw_image(img_path, bboxes):
image = Image.open(img_path)
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(image)
for xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax in bboxes:
draw.rectangle([xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax], outline='red', width=4)
cv2.imshow('result', cv2.cvtColor(np.array(image), cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR))
cv2.waitKey(0)
def detect_face(image, shrink):
h, w = image.size
if shrink != 1:
image = image.resize((int(w * shrink), int(h * shrink)), Image.ANTIALIAS)
img = np.array(image)
img = np.swapaxes(img, 0, 2)
img = np.swapaxes(img, 0, 1)
img = img[[2, 1, 0], :, :] # RGB->BGR
img -= np.array([104., 117., 123.])[:, None, None]
img = img * 0.007843
result, = exe.run(infer_program,
feed={feeded_var_names[0]: img[None, ...]},
fetch_list=target_var)
result = np.array(result)
det_conf = result[:, 1]
det_xmin = (w * result[:, 2]) / shrink
det_ymin = (h * result[:, 3]) / shrink
det_xmax = (w * result[:, 4]) / shrink
det_ymax = (h * result[:, 5]) / shrink
return np.column_stack((det_xmin, det_ymin, det_xmax, det_ymax, det_conf))
def infer(image_path, confs_threshold=0.15):
image = Image.open(image_path).convert('RGB')
shrink, _ = get_shrink(image.size[1], image.size[0])
dets = detect_face(image, shrink)
dets = dets[dets[:, 4] >= confs_threshold]
draw_image(image_path, dets[:, :4])
if __name__ == '__main__':
infer('test.jpg')
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
- Output
Detected faces are drawn in red boxes. The prediction result image is displayed in a window.
Result¶
Example output image after detection:
